It's all about the classical music composers and their works from the last 400 years and much more about music. Hier erfahren Sie alles über die klassischen Komponisten und ihre Meisterwerke der letzten vierhundert Jahre und vieles mehr über Klassische Musik.
Total Pageviews
Thursday, January 4, 2018
Robert Schumann - His Music and His Life
Robert Schumann was a German composer and critic born in Zwickau on June 8, 1810. A quirky, problematic genius, he wrote some of the greatest music of the Romantic era, and also some of the weakest. Severely affected by what was most likely bipolar disorder, he achieved almost superhuman productivity during his manic periods. His life ended early and miserably with a descent into insanity brought on by syphilis. He did his best work when younger, in small forms: piano pieces and songs.
Early Years Of Study
Schumann's bookseller father was also a novelist and translator of Walter Scott and Byron; highly nervous, he married a violently passionate woman, and Schumann was brought up in an environment both literary and unstable. He began piano lessons at seven, and studied Latin and Greek in school in Zwickau, developing a keen interest in literature and in writing as he entered his teens. He continued to develop as a pianist and wrote novels. When he was 16 his father died and in the same month his sister committed suicide. His father had stipulated that for Robert to receive his inheritance he had to take a three-year course of study at the university level, and the next year Schumann enrolled as a law student at the University of Leipzig. He spent his time reading Jean Paul Richter and soon became a piano student of (and border with) Friedrich Wieck, whose daughter Clara, then nine, he would eventually marry. He developed a consuming interest in the music of Schubert, which opened a window on his own creative yearnings.
In 1830, Schumann opted out of law and resumed his studies with Wieck. Despite incessant practice, he never became the virtuoso pianist he hoped to be, owing to a "numbness" in the middle finger of his right hand. The problem may have resulted from his use, over Wieck's objection, of a splint contraption to strengthen the hand, or from mercury poisoning related to the treatment of syphilis, which he probably contracted in his teens. Fortunately, he would not need to be a virtuoso — because he married one.
Music — And Trouble — In The 1830s
The 1830s were turbulent for Schumann. He fought with Wieck over his training and his relationship with Clara, which Wieck opposed. Under stress, he drank and smoked heavily and suffered his first bouts of depression. Gradually, Schumann let go of the dream of keyboard virtuosity and became active as a critic, for which he was, during his lifetime, as well known as he was for his music. Simultaneously, he developed into quite a capable composer.
In 1834 he founded the Neue Zeitschrift für Musik, turning it into a platform for his philosophizing on the music of the past and present and for notices and analyses of new works. Among his own important works of the decade were the majority of the pieces that established his reputation as a composer for the piano: Carnaval, the Davidsbündler Tänze, the Symphonic Etudes, the Fantasy in C, Kinderszenen (Scenes from Childhood), Kreisleriana, and others. During this time, he befriended Chopin and Mendelssohn.
Marriage, Music, And Mania
By 1840, Clara Wieck, 20, was a distinguished pianist and had been in the public eye for more than a decade. Schumann's marriage to her — which took place a year after he prevailed in a lawsuit against her father — resulted in an enormous creative outpouring. First came the "year of song." Anticipating marriage in a decidedly lyrical state of mind, Schumann focused his pent-up emotion on vocal music, composing nearly 140 songs in 1840, most of them in the anxious months before August, when the marriage permission suit he and Clara had filed against her father was decided in their favor. The following year, in a mood of celebration, he turned to the orchestra. His works included two symphonies — No. 1 in B-flat and No. 4 in D minor — as well as Overture, Scherzo and Finale, and a Fantasie in A minor for piano and orchestra. In 1842 Schumann focused on chamber music, composing three string quartets, the often heard Piano Quintet in E-flat, and the wonderful Piano Quartet in E-flat.
Such feverish concentration on a single genre at a time can be seen as typical manic behavior. The other side of the coin — phobias and terrifying slides into depression — turned up as the 1840s wore on, leaving the composer incapacitated. At the end of 1844 Schumann and Clara moved to Dresden, at one of the lowest of his low points. During his next few years, he completed the Piano Concerto in A minor, his Symphony No. 2 in C, his one opera, Genoveva, and an extraordinary dramatic poem based on Byron's Manfred.
Düsseldorf And Downhill
In 1850, Schumann accepted a position as municipal music director in Düsseldorf. One of the first works he composed after his arrival was the Symphony No. 3 in E-flat, the Rhenish, inspired by the majestic Cologne Cathedral. During the three seasons he held the job, Schumann experienced difficulties with city administrators and ultimately, owing to his increasingly erratic behavior on the podium, lost the respect of the orchestra and chorus. He was fired in the fall of 1853. A bright spot during that sad season was the time the Schumanns spent with the renowned violinist Joseph Joaquim and the 20-year-old Johannes Brahms, whose budding genius Schumann immediately recognized.
During the winter of 1854, Schumann's insanity manifested itself dramatically: He heard "angelic" voices that quickly morphed into a bestial noise of "tigers and hyenas." On a February morning he walked to a bridge over the Rhine and threw himself in; he was rescued by fishermen. Insisting that for Clara's protection he be institutionalized, he was placed in a sanatorium. His doctors prevented Clara from seeing him for more than two years, until days before his death.
The Music Of Poetic Personalities
Schumann's literary sensitivity and introspective nature led him to imbue nearly everything he wrote with personality — in the case of his best songs and piano pieces, often the multiple sides of his own personality. Nearly all of his piano music is referential, attempting to embody emotions aroused by literature or to characterize actors' interactions in some ongoing novel or lyric poem of the mind. One of Schumann's favorite conceits was the "Davidsbund" ("Tribe of David"), peopled by imaginary characters who, like the biblical David, were willing to stand up to the artistic Philistines of the day. The members of this society included Meister Raro, probably an idealization of his teacher and father-in-law, as well as Schumann's two major personae: the impetuous extrovert Florestan and the pale, studious, introverted Eusebius. The Davidsbündler Tänze (Dances of the Tribe of David) specifically chronicles an emotional and musical journey with these two alter egos at the wheel — but so do most of Schumann's works, especially those for piano.
Schumann's lyrical, intense musicality produced some of the most beautiful and moving lieder in the repertoire. His Dichterliebe (Poet's Love), a setting of 16 poems by Heinrich Heine, is his best-known song cycle and a supreme achievement in German lied. Other cycles include Frauenliebe und Leben (Women's Love and Life) and two sets titled Liederkreis (one to poems of Heine, one to poems of Joseph von Eichendorf). There is a substantial amount of chamber music; the best pieces are the Piano Quintet (the first piece ever written for that complement), the Piano Quartet, and the Three Romances for oboe and piano.
As a symphonic composer Schumann sports a long rap sheet: awkwardness in larger forms, muddy scoring, excessive doublings that always sound a little out of tune. But he was capable of achieving splendid orchestral effects, and his Third and Fourth Symphonies also reveal original and innovative approaches to form. In an effort to reinforce a feeling of unity in the Fourth Symphony, he specified that its four movements be played without a break, with the aim that the entire work would form a large, cyclical structure. The underlying unity of the piece asserts itself in the treatment of the key and in the thematic linking of the last movement to the first, and of parts of the third movement to the second. The material is so closely knit that musicologists have come to regard it as a landmark in the history of the genre. Of the concerted works, the Piano Concerto is Schumann at his best. The Cello Concerto is a solid piece but the Violin Concerto, a late work of troubled delicacy, requires very sympathetic treatment to be effective. None of Schumann's efforts for the stage has found a place in the repertoire.
There is little doubt that Schumann will remain a canonic figure, though if quality of work is the only gauge, his importance has long been overrated. His abilities, at times, fell short of his ambitions, but he brought enthusiasm and a rare poetic genius to everything he attempted. As a critic he was remarkably astute in some judgments, wildly off the mark in others, and in all cases generous. He never became a great pianist, was a failure as a conductor, and at times was not even a very good composer. But his entire being was music, informed by dream and fantasy. He was music's quintessential Romantic, always ardent, always striving for the ideal.
(Ted Libbey is the author of "The NPR Listener's Encyclopedia of Classical Music")
13 reasons you should be friends with a musician
By ClassicFM London

396
 |  |  |
Musicians: they’re spontaneous, fun and can be used as a walking record player. Here are all the reasons you should make friends with a muso.
1. They make ‘Happy Birthday’ 150 per cent better at your birthday parties
Being sung to can be toe-curlingly embarrassing. But your new musician friend is guaranteed to jazz up your birthday serenade with a strum-heavy accompaniment and lots of super-understated harmonies.
2. They can play beautiful music at your wedding.
Pachelbel’s Canon? The Blue Danube? The theme tune to Love Actually? Whatever you fancy on your big day, your mate will be there for you with their instrument and buckets of wedding repertoire on tap, plus a subtle plug or ten for their upcoming concert.
3. You’ll get a whole new friendship group
One word: BANDMATES. Work, hobbies and a social life can be tough to juggle. But with your new muso pal, you’ll have a brand-new group of friends who turn up to your garage every Thursday to practise and steal your beers.
4. When life gets overwhelming, they can play nice relaxing music for you
Sure, life is stressful. But it’s 80 per cent less traumatic when your mate starts practising Debussy and Chopin in the next room.
5. They make you realise money doesn’t matter
Who needs $$$ when you’re surrounded by the beauty of music? Your poor, struggling muso pal will help you remember what’s really important in life.
6. You’ll get to go to loads of great gigs
Queuing online for Joshua Bell tickets is, let’s face it, a total bore. Get yourself a musician friend, and go to all their cheap concerts in weird falling-down pubs.
7. You’ll develop a great taste in music
Worried that your taste in music is lacking in refinement and variety? Befriend a musician, and borrow all their old records.
8. You’ll get a fun new side project
Getting bored of your old job? Find a musician friend, and you’ll get an awesome new job as their manager and social media editor.
9. You’ll learn to judge talent show entrants with real music knowledge
That singer on The X Factor? “Pfft! People only like her because she uses a vibrato wide enough to scare Bach out of his grave,” you’ll learn to say.
10. You’ll always have a driving buddy
No one likes driving alone – and a musician needs transport. Offer to take them to all their gigs ever, and you’ll never be without your Kenickie.
11. They’ll teach you the language of music
Found a muso who doesn’t speak your language? No matter! Music is a universal language, and befriending that Italian violist will help you understand that music equals communication, and words are largely unimportant.
12. You’ll have endless surprising adventures
Musicians are highly unpredictable creatures – one minute, they’ll be able to come to your mum’s 60th birthday party, the next, they’ll be jetting off to Croatia to give a strings masterclass. If you love to be surprised, find yourself a muso friend.
13. You’ll do loads of mid-week drinking
Bored of the usual Friday and Saturday night pub trips? Befriend that trombone player you always see at the supermarket, and get ready to indulge in a serious post-concert Monday night drinking sesh.
Wednesday, January 3, 2018
Thursday, December 21, 2017
Andrea Bocelli & David Foster My Christmas Live At The Kodak Theatre
Merry Christmas / Frohe Weihnachten
Saturday, December 9, 2017
22 of the best insults in classical music
If you thought classical music was all about peaceful tunes and harmony, think again. The gloves are off and the claws are out as we explore some of the rudest, most insulting composer put-downs in the history of classical music.




1. Rossini
"What a good thing this isn't music." Rossini on Berlioz's Symphonie Fantastique



2. Copland
"Listening to the fifth symphony of Ralph Vaughan Williams is like staring at a cow for 45 minutes." - Copland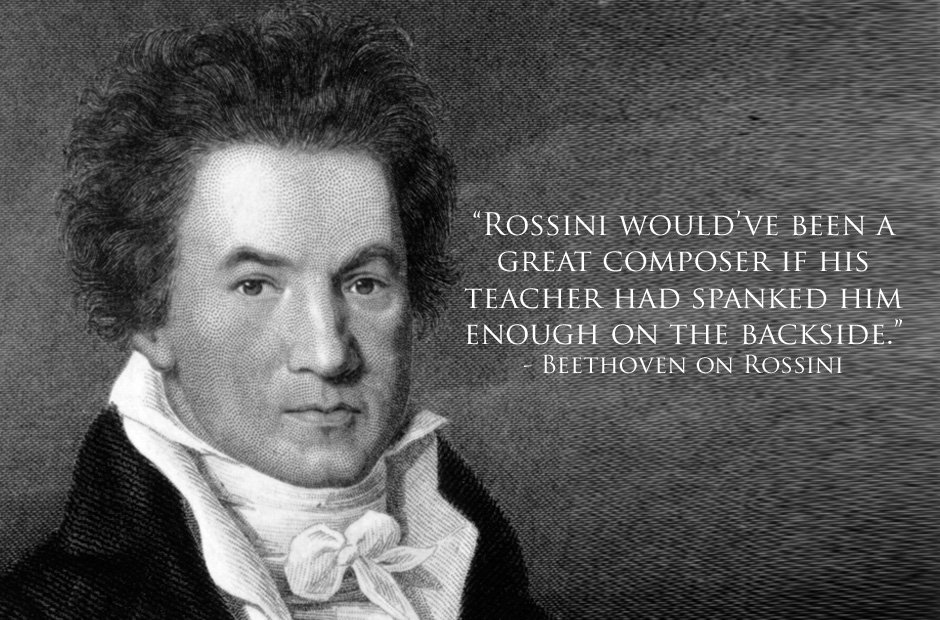



3. Beethoven
"Rossini would have been a great composer if his teacher had spanked him enough on the backside." Beethoven on Rossini



4. Beethoven
"I like your opera - I think I will set it to music." Beethoven



5. Rachmaninov
"He was a six and a half foot scowl." Stravinsky on Rachmaninov



6. Messiaen
"All you need to write like him is a large bottle of ink." Stravinsky on Messiaen



7. Tchaikovsky
"It is the most insipid and base parody on music." Tchaikovsky on Mussorgsky's Boris Godunov



8. Stravinsky
"It's beautiful and boring. Too many pieces finish too long after the end." Stravinsky on Handel's Theodora



9. Elgar
"The musical equivalent of St Pancras Station." Sir Thomas Beecham on Elgar



10. Wagner
"Wagner has beautiful moments, but awful quarters of an hour." Rossini on Wagner



11. Berlioz
"A tub of pork and beer." Berlioz on Handel



12. Debussy
The audience expected the ocean. Something big, something colossal, but there were served instead with some agitated water in a saucer." Louis Schneider on La Mer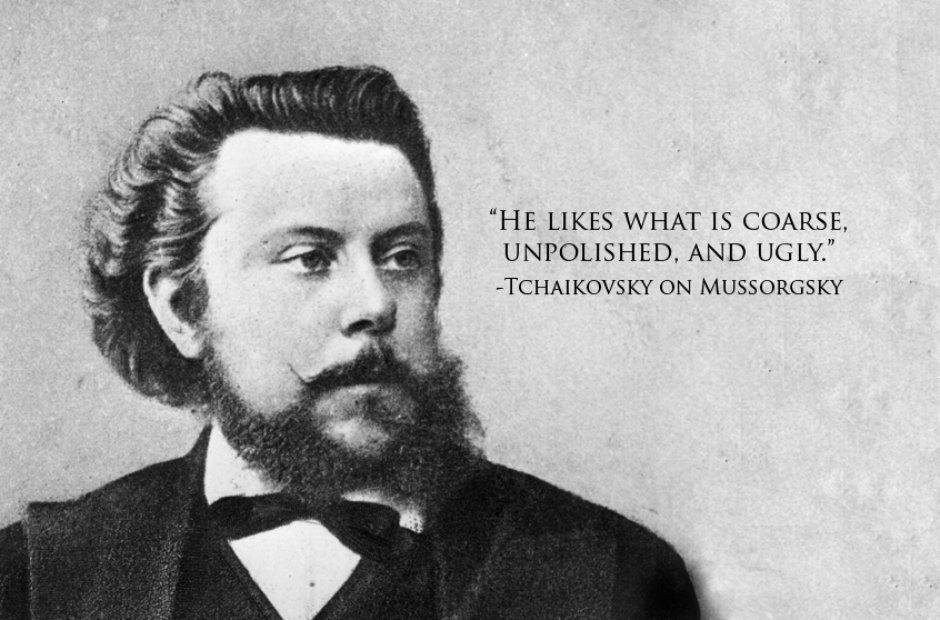



13. Mussorgsky
"He likes what is coarse, unpolished, and ugly." Tchaikovsky on Mussorgsky



14. Chopin
"A composer for one right hand." Wagner on Chopin



15. Clara Schumann
"He gives me the impression of being a spoilt child." Clara Schumann on Liszt.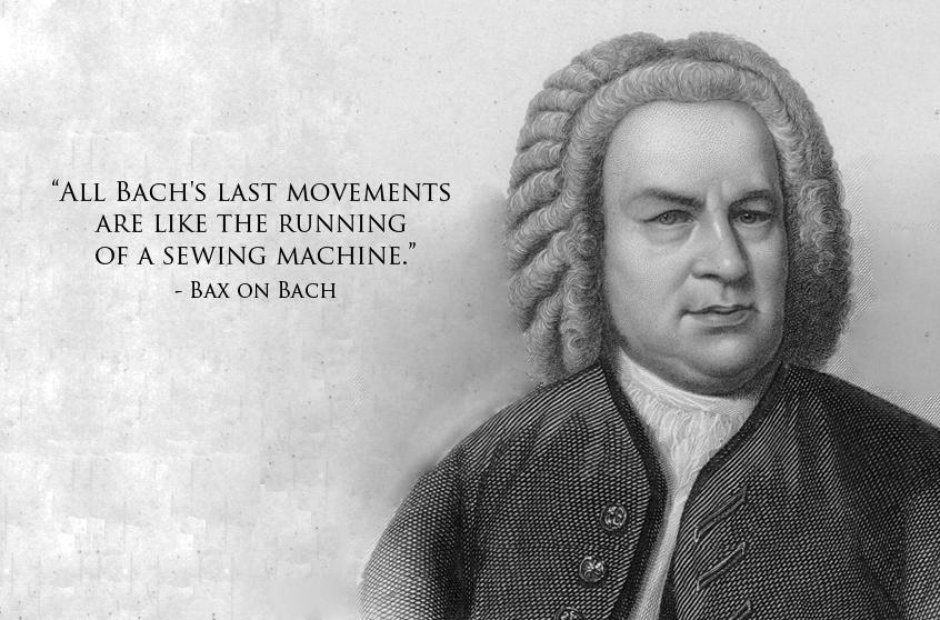



16. Bach
"All Bach's last movements are like the running of a sewing machine." Bax on Bach



17. Brahms
"What a giftless bastard!" Tchaikovsky on Brahms



18. Handel
"Handel is only fourth rate. He is not even interesting." Tchaikovsky on Handel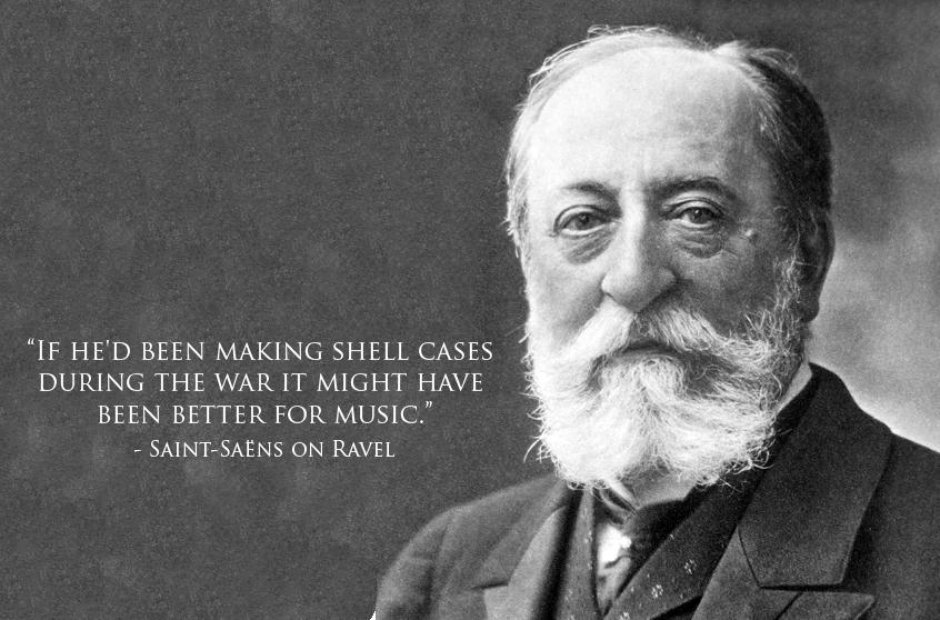



19. Saint-Saens
"If he'd been making shell cases during the war it would have been better for music." Saint-Saëns on Ravel



20. Britten
"I liked the opera very much. Everything but the music." Britten on Stravinsky's The Rake's Progress



21. Strauss
"He'd be better off shovelling snow than scribbling on manuscript paper." Richard Strauss on Schoenberg



22. Prokofiev
"Bach on the wrong notes."
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)

