It's all about the classical music composers and their works from the last 400 years and much more about music. Hier erfahren Sie alles über die klassischen Komponisten und ihre Meisterwerke der letzten vierhundert Jahre und vieles mehr über Klassische Musik.
Total Pageviews
Monday, January 27, 2025
Joseph Joachim Romanze in C
Friday, November 1, 2024
The 10 Most Beautiful Piano Quintets in Classical Music
by Hermione Lai, Interlude
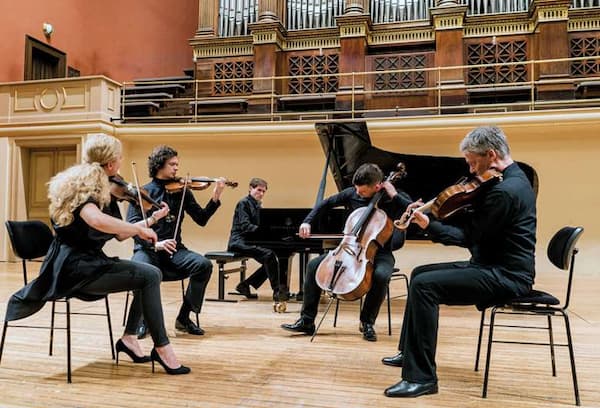

Piano Quintet
Interestingly, piano quintets are less common than keyboard chamber music for smaller ensembles, probably because of the challenges of clearly defining the relationship between piano and strings. Piano quintets had been written before, but it was only by the middle of the 19th century that this particular genre took on the seriousness of other prestigious chamber music genres.
Are you ready to explore the 10 most beautiful piano quintets in standardised scoring? Once again, we do have a rather substantial number of works on offer, and all playlists of this kind are subject to personal taste. However, one thing we can probably agree on is that the Schumann E-flat Major Piano Quintet is one of the greatest works in this genre.
Robert Schumann: Piano Quintet in E-flat major, Op. 44
Robert Schumann (1810-1856) was rather severely harassed by his sceptical father-in-law. In order to prove potential earnings from composition, Schumann wrote over one hundred songs in 1840. In 1841, he wrote nothing but symphonic works, and in 1842, he turned his attention towards chamber music. To prepare, he studied quartets by Mozart, Haydn, and Beethoven, and composed a piano trio, three string quartets, a piano quartet, and the Piano Quintet Op. 44.
Dedicated to his wife Clara, Schumann featured a complete string quartet with added piano. The opening “Allegro brillante” features a bold and sparkling musical idea that organically expands. Almost immediately, however, this is contrasted by a soft and tender dialogue between the viola and the cello. In due course, both themes are extensively fragmented and subjected to far-reaching modulations. The second movement unfolds in the manner of a funeral march, with a dark and mysterious melody accompanied by sobbing musical rhythms.

Robert Schumann, 1850 © pianolit.com
The “Scherzo” joyously and exuberantly presents ascending and descending major scales, contrasted by two “Trios,” which sound a lyrical canon and Hungarian gypsy music, respectively. Schumann’s contrapuntal and expressive prowess emerges in the concluding “Allegro”, as he blends strict canonic and fugal passages with passages of nervous lyricism. The coda is cast as a double fugue and breathtakingly combines the main themes of the first and last movements.
Johannes Brahms: Piano Quintet in F minor, Op. 34
In terms of the Piano Quintet, it is difficult to say Schumann without also saying Brahms. However, the marvellous Brahms Piano Quintet started out as a quintet for two violins, viola, and two cellos. Clara Schumann was enthusiastic and praised that “inner strength and richness written for the instruments.” However, when Brahms sent it to Joseph Joachim, the famous violinist had reservations and suggested that it “lacked charm and sounded artificial in spots.”

Clara Schumann and Johannes Brahms
Not entirely confident in his abilities, Brahms reworked the piece as a piano sonata for two pianos. When he played it with Clara, she was overwhelmed by the music’s grandeur but refused to call it a sonata. As Clara wrote, “it is so full of ideas that it requires an orchestra for its interpretation.” Brahm once again started to transform the work, and it was the conductor Hermann Levi who suggested that it should be recast as a piano quintet.
In the end, the piano quintet is a hybrid of two earlier versions, combining Brahms’ youthful exuberance with sophisticated musical textures and a logical way of constructing motives and their subsequent development and continuation. When Levi heard the finished composition in 1865, he wrote, “The quintet is beautiful beyond measure; Out of the monotony of the two pianos a model of tonal beauty has arisen; a restorative for every music-lover, a masterpiece of chamber music.”
Gabriel Fauré: Piano Quintet No. 1 in D minor, Op. 89
Not unlike Brahms, it took Gabriel Fauré a number of years before he came to terms with his first Piano Quintet. First published in 1906, drafts for the work actually date from 1887. Four years later, Fauré contemplated the addition of a second violin to what might have been a third piano quartet. After drafting two movements, he put the work aside once more and only returned to work again in 1903. The composer referred to the work as “this animal of a quintet”, and the piece was finally completed towards the end of 1905.

John Singer Sargent: Gabriel Fauré, 1896
The work is dedicated to Eugène Ysaÿe, and a first performance in Brussels with the Ysaÿe Quartet in March 1906 was repeated in Paris the following month. Commentators heard a “strangely inward melancholy” possibly connected to some medical problems the composer experienced during the 1880s. Fauré experienced dizziness and severe headaches, and suffered from depression possibly related to the death of his father in 1885. He also started to experience hearing loss, which began to affect him in earnest in 1902. Fauré grew tired “of repeating himself endlessly in his music,” but the Op. 89 Piano Quintet stands apart from his other chamber works, including his 2nd Piano Quintet, Opus 115.
Jean Sibelius: Piano Quintet in G minor

Jean Sibelius
On 19 January 1890, Ferruccio Busoni performed the Piano Quintet in E minor, Op. 5 by the Norwegian composer Christian Sinding at the Gewandhaus in Leipzig. In the audience, by invitation from Busoni, was Jean Sibelius. It has long been suspected that this occasion provided the impulse for Sibelius to start work on his own five-movement Piano Quintet in G minor. The work was completed in April 1890, and the first concert performance took place in Helsinki, with Busoni playing the piano part.
While Busoni greatly admired the composition, Sibelius’ former composition teacher, Martin Wegelius, was highly critical of the piano writing, especially in the first movement. As he commented, “his curious whims and fancies have obscured his real self.” Surprisingly, the “Finale” was never performed during the composer’s lifetime, and it first sounded in public only in 1965. A scholar writes, “maybe Sibelius feared that it would never actually be performed and wished to salvage some of its musical material; or perhaps he felt that he had not exhausted the potential of its themes.” In the event, the Piano Quintet is one of the most impressive chamber works by Sibelius, with the composer “striving for a new ruggedness and severity of mood.”
Antonín Dvořák: Piano Quintet in A Major
Following in the footsteps of his idol Johannes Brahms, Antonín Dvorák (1841- 1904) exhibited a heightened sense of musical insecurity. The Piano Quintet in A Major, published as Op. 5 in 1872, makes a convincing case in point. Although received enthusiastically by critics and audiences alike, Dvorák remained highly dissatisfied with the work and destroyed the manuscript soon after its premiere.
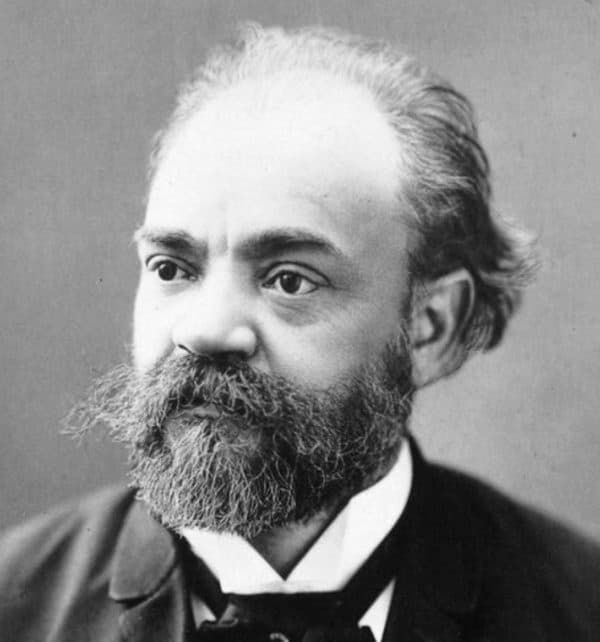

Dvořák in New York, 1893
Fifteen years later, the composer reconsidered and began to make extensive revisions to the work. However, rather than submitting the revised work for publication, he cast it aside for good and instead worked on a brand new quintet in the same key. The resulting Piano Quintet in A Major, Op. 81 not only secured Dvorák’s international reputation but also produced a distinctive masterpiece of Nineteenth-Century chamber music.
The gently flowing piano accompaniment provides the colouristic background to one of Dvorák’s most expressive and lyrical melodies, stated in the cello. However, this sense of tranquillity is suddenly interrupted by a rhythmically animated transition in the minor mode that propels the music forward. This process is once repeated before the viola sings another lyrical melody. Subsequently, both themes are thoroughly developed—relying predominantly on the first and second violin—before a rhapsodic recapitulation feeds into a sparkling and virtuosic coda. The second movement invokes a Ukrainian lament, known as “Dumka,” and the ”Scherzo” is cast in the style of a Bohemian folk dance called “Furiant.” Not to be outdone, the “Finale” presents yet another vigorous dance, a Polka.
Edward Elgar: Piano Quintet in A minor, Op. 84
Edward Elgar was born in a small village and initially earned his living by working in the office of a local solicitor. He received no formal musical training, but nevertheless succeeded his father as organist and played the violin in an orchestra at Birmingham. His early attempts at composition are patterned after the music of Schumann, Mendelssohn, Brahms and Wagner, but plans to attend the Leipzig Conservatory were never realized.
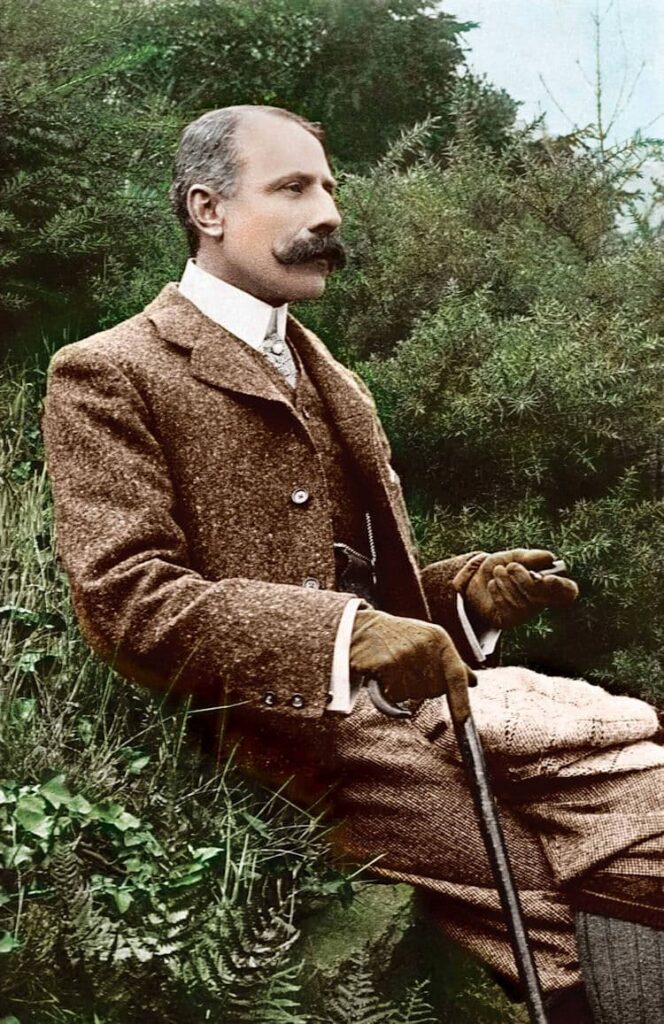

Edward Elgar
With his A minor quintet, one of three chamber compositions dating from the concluding years of WWI, Elgar returned to the themes and musical aspirations of his youth. Unwilling to participate in modernist musical experimentations, Elgar provided a summary review of 19th-century European musical practices from a distinctly English perspective.
The first movement opens with a hauntingly beautiful introduction that canvasses a slow-moving melodic fragment played by the piano against a rhythmically animated commentary given by the strings. Sounding at once rhapsodic and almost improvisatory in nature, Elgar himself described the introduction as “ghostly stuff.” The opening movement clearly pays homage to Brahms’s musical personality, while the “Adagio” explores the musical tensions of an extended emotional narrative. The final movement, which also relies on a slow musical introduction, provides the fitting nostalgic conclusion to Elgar’s musical gesture of resignation.
Béla Bartók: Piano Quintet in C Major
Let’s now turn to Béla Bartók (1881-1945), one of the most influential figures in the history of classical music. Composer, performer, educator, and ethnomusicologist, Bartók powerfully shaped the way subsequent generations approached and listened to music. Bartók displayed great musical talent at an early age. He could distinguish between different tunes and rhythms before he started talking, and by age 4 he had roughly 40 pieces in his piano repertory.
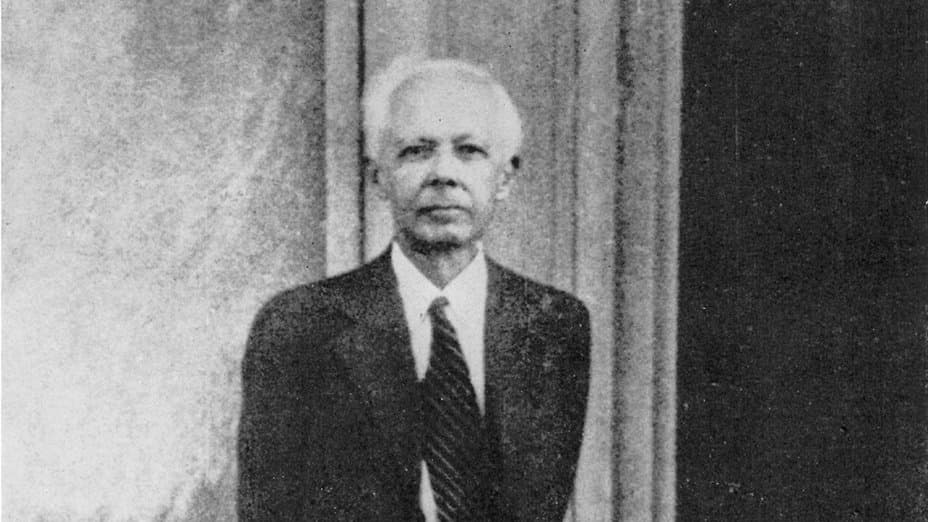

Béla Bartók in New York, 1944
Bartók composed the four movements of his Piano Quintet in 1903 and 1904, and thematically, they are reminiscent of the music of Johannes Brahms and Richard Strauss. Yet, Bartók was not slavishly following traditional compositional standards. In the final two movements, we find early inclusions of folk elements, resulting in a distinctive Hungarian flavour.
A tightly organised formal structure builds on the continual repetition and variations of themes and unfolds within a highly flexible tonal space. The consistent use of asymmetrical rhythms completes a vocabulary of stylistic features that would soon become familiar elements of Bartók’s expressive language. For one reason or another, Bartók had to be persuaded not to destroy this composition. Thankfully, he took the manuscript with him to the United States, where it was published after his death.
Dmitry Shostakovich: Piano Quintet in G minor, Op. 57
My list of top 10 Piano Quintets must necessarily include the G-minor work by Dmitry Shostakovich. It was composed during the summer of 1940 and written for the Beethoven Quartet and himself. The work followed on the heels of his Sixth Symphony, a work that received a rather mixed reception. The success of the Piano Quintet, however, was unqualified and long-lasting. In fact, the composition was awarded a Stalin Prize of 100,000 rubles.
Dmitry Shostakovich, 1925
Robert Matthew-Walker writes, “a glance at the list of movements might lead one to imagine that this is a neoclassical work, but its direct emotional power and thematic integration place it on altogether a higher level than mere pastiche.” The opening movement titled “Prelude” opens with a declamatory three-note cell that provokes an impassioned response from the strings. The four-voiced “Fugue” begins with a strict exposition by muted strings that build into an elegiac web of sound, eventually joined by the piano adding a bass line.
The music continues immediately with a whirlwind “Scherzo,” with the piano presenting a witty theme that interacts with the strings. The first trio sounds a gypsy-like air, while the second involves playful pizzicato. A cool and relaxed “Intermezzo” unfolds over a walking bass accompaniment in the cello, with the remaining strings sounding a bitter-sweet counterpoint. In the “Finale,” the piano sounds a gentle theme over an animated accompaniment. Once the mood quietens, the work returns to the impassioned beginning but ends in a quiet and contented close.
Nicolai Medtner: Piano Quintet in C Major
Nicolai Medtner, who died in London on 13 November 1951, was one of the very last Romantic composer-pianists. Overshadowed by his contemporaries Scriabin and Rachmaninoff, Medtner made the piano the focus of his creative activity and frequently tempered a Russian spirit with music firmly rooted in the Western classical tradition. A scholar writes, “Fully developed almost from the time of his first published works, his musical idiom changed very little throughout his career, and his entire output is remarkably consistent in quality.”
Sadly, the Piano Quintet in C Major was Medtner’s final composition on which he had worked intermittently for almost 45 years. Initial sketches date from 1904 and 1905, and the work was completed towards the end of 1948. A severe heart attack prevented the composer from rehearsing and recording it. Jeremy Lee writes, “Fervent, sincere, personal, and above all intensely soulful, Medtner’s Piano Quintet certainly is one of the most deeply satisfying works ever written.”
Grażyna Bacewicz: Piano Quintet No.1
Let me conclude my list of the 10 most beautiful piano quintets with a work by the Polish violinist, pianist, and composer Grażyna Bacewicz (1909-1969). One of the most significant voices in European music of the twentieth century, she studied with Nadia Boulanger and the violinists André Touret and Carl Flesch. Her compositional development initially focused on clarity, wit and brevity, while her works from the time of World War II “show a greater muscularity and daring disregard for traditional classical structures.”

Grażyna Bacewicz
Her first piano quintet dates from 1952, and it presents a sound world that mediates between folkloric impulses “and the developmental rigour of classical principles.” It is a highly personal work, and you can hear the use of folk materials directly and indirectly. I hope you enjoyed my selections, but for every piano quintet featured, I had to sadly neglect some equally wonderful choices. The Borodin quintet is fantastic, as are the piano quintets by Rubinstein, Franck, Bruch, Suk, Vierne, Granados, Reger, Amy Beach, Bax, Dohnányi, Milhaud, and many others; would you like to see some of them featured?
Friday, June 7, 2024
10 Pieces of Classical Music About Friendship
by Emily Hogstadt, Interlude
Today, we’re looking at ten pieces of classical music that reflect on composers’ friendships in some way, whether it’s Beethoven’s dedication of a private string quartet to a friend or Elgar’s extravagant orchestral puzzle dedicated to his friends.
Enjoy!
Ludwig van Beethoven: String Quartet No. 11 (1810-11)
Beethoven’s eleventh quartet was a unique piece from the start: he wrote in a letter to a friend that “The Quartet is written for a small circle of connoisseurs and is never to be performed in public.”
In it, Beethoven allowed himself to experiment and take risks. It was written the year after Napoleon invaded Vienna when the routines of people in the city had been shattered, so there weren’t many audiences interested in coming to performances, anyway.

Nikolaus Zmeskall von Domanovecz © Wikipedia
Beethoven dedicated this work to his friend, Count Nikolaus Zmeskall von Domanovecz. Zmeskall was a civil servant and an amateur cellist who hosted gatherings in his home where chamber music was performed. These house concerts were the first place where much of Beethoven’s later chamber music was first heard.
Frédéric Chopin: Variations on “Là ci darem la mano” (1827)
Frédéric Chopin had such an intense friendship with political activist Tytus Woyciechowski that some scholars have recently claimed that the two had a romantic relationship.

Tytus Woyciechowski © Wikipedia
Some historians have protested, but regardless of the truth, Chopin certainly did write some very intimate letters to Woyciechowski, including this one in 1830:
I will go and wash. Don‘t kiss me now because I haven‘t yet washed. You? Even if I were to rub myself with Byzantine oils, you still wouldn’t kiss me, unless I compelled you to do so with magnetism. There is some sort of force in nature. Today you will dream that you‘re kissing me. I have to pay you back for the nasty dream you brought me last night…
Three years earlier, Chopin had written a series of variations for piano on an aria from Mozart’s opera Don Giovanni and dedicated it to Woyciechowski.
The two friends eventually drifted apart, but they always remained in each other’s hearts. Woyciechowski eventually named one of his children after Chopin.
Felix Mendelssohn: Allegro Brillant (1841)
Since he was very young, composer Felix Mendelssohn was a close colleague of prodigy pianist Clara Wieck Schumann (the woman who eventually married composer Robert Schumann).
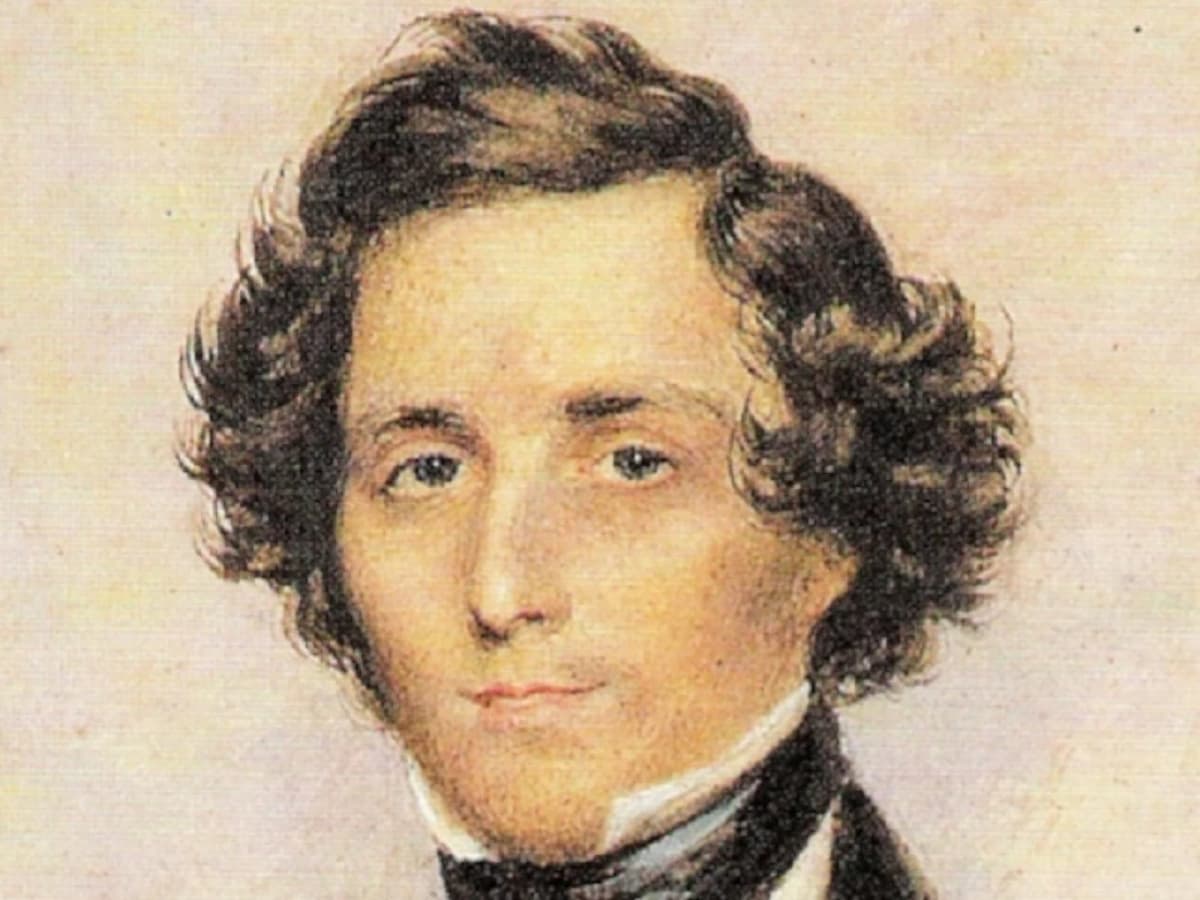

Felix Mendelssohn © U.S. Public Domain
In 1835, Mendelssohn was named music director of the Gewandhaus orchestra in Leipzig. Wieck, born in 1819, was a popular up-and-coming Leipzig-born piano prodigy, so the two often worked together professionally.
As a token of his admiration, in 1841, the year after her marriage to Robert Schumann, Mendelssohn wrote the dazzling Allegro Brillant for piano four-hands for Clara.
As a token of respect for his friend’s ability, the Allegro Brillant is devilishly difficult.
Johannes Brahms: Violin Concerto (1878)
Another musician in the Mendelssohn/Schumann social circle was a Hungarian violinist named Joseph Joachim.
In 1844, at the age of twelve, Joachim gave the first performance in decades of Beethoven’s violin concerto. This performance helped to kick off an entire reappraisal of the work. (By the way, the conductor at that concert? None other than Felix Mendelssohn!)

Joseph Joachim, 1853
When they were young, Joseph Joachim became great friends with pianist Johannes Brahms, and tried to help promote Brahms’s career. In fact, Joachim made the introductions between Brahms and the Schumanns, which became one of the most formative experiences of Brahms’s life.
Brahms and Joachim continued to be friends for many years (although their relationship had its ups and downs).
When Brahms wrote his violin concerto, he wrote it for Joachim, consulting extensively with him via mail. It shouldn’t be a surprise that the finale is extremely Hungarian in character. Joachim reciprocated the friendly gesture by writing the cadenza in the concerto, which is still the only one regularly played.
Edward Elgar: Enigma Variations (1898-99)
When Edward Elgar published his Enigma Variations for orchestra, he included a dedication: “to my friends pictured within.”
Each movement is a portrait of someone in his life, complete with musical puzzles and extra-musical references that have kept musicologists and nerdy listeners debating as to their identities for generations.
In 1911, he expanded on his dedication:
This work, commenced in a spirit of humour & continued in deep seriousness, contains sketches of the composer’s friends. It may be understood that these personages comment or reflect on the original theme & each one attempts a solution of the Enigma, for so the theme is called. The sketches are not ‘portraits’ but each variation contains a distinct idea founded on some particular personality or perhaps on some incident known only to two people. This is the basis of the composition, but the work may be listened to as a ‘piece of music’ apart from any extraneous consideration.
Sergei Rachmaninoff: Piano Concerto No. 2 (1900-1901)
Rachmaninoff’s second piano concerto may be among his most popular works today, but it only came to life after a lot of blood, sweat, and tears…and one especially helpful friend.

Nikolai Dahl © Wikipedia
To make a long story short, Rachmaninoff was so traumatized by the failure of his first symphony in 1897 that it triggered a mental breakdown. He wasn’t sure if he’d be able to compose again.
After several years of writers’ block, in early 1900, Rachmaninoff finally began going to a neurologist and family friend named Nikolai Dahl. Dahl helped him process the failure of his symphony and feel comfortable composing again. In gratitude, Rachmaninoff dedicated his second concerto to him.
The concerto is lush, deeply emotional, and beautifully paced and proportioned. Rachmaninoff toured the world playing and promoting it, ensuring its spot in the classical music canon.
George Enescu: Violin Sonata No. 3 (1926)
In 1926, violinist Franz Kneisel died. Kneisel had had a remarkable career. He was born in Bucharest, Romania, and studied music there and in Vienna. He became a concertmaster when he was just a teenager; he was later handpicked to serve in that position with the fledgling Boston Symphony, and he also founded the first professional string quartet in the United States, the Kneisel Quartet, which performed in America for decades.
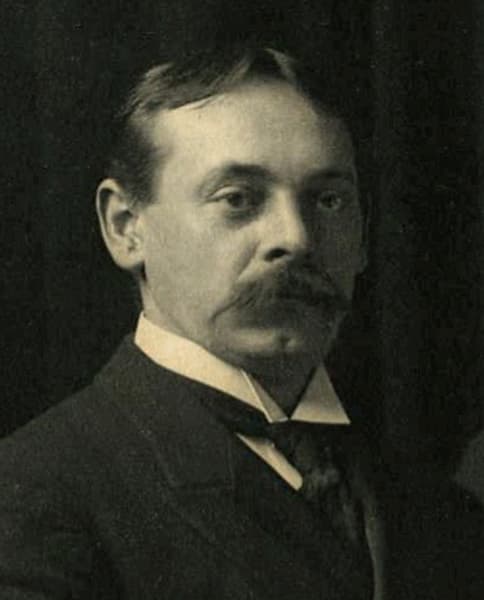

Violinist Franz Kneisel in 1902 © Wikipedia
So when Kneisel died in 1926, he was very famous. Composer and violinist George Enescu – a fellow Romanian musician – decided to pay homage to Kneisel’s origins by posthumously dedicating a violin sonata “in Romanian Folk Style” to him. It became Enescu’s most popular work.
Karol Szymanowski: Violin Concerto No 2 (1932-33)
Ukrainian violinist Paweł Kochański became sick with cancer in his forties. Cancer treatments were relatively limited at the time, and he would die at the age of 46 from the disease.
Before he died, however, he commissioned a violin concerto from his friend, Polish composer Karol Szymanowski. Szymanowski was deeply inspired by the request and wrote the concerto in a matter of weeks.
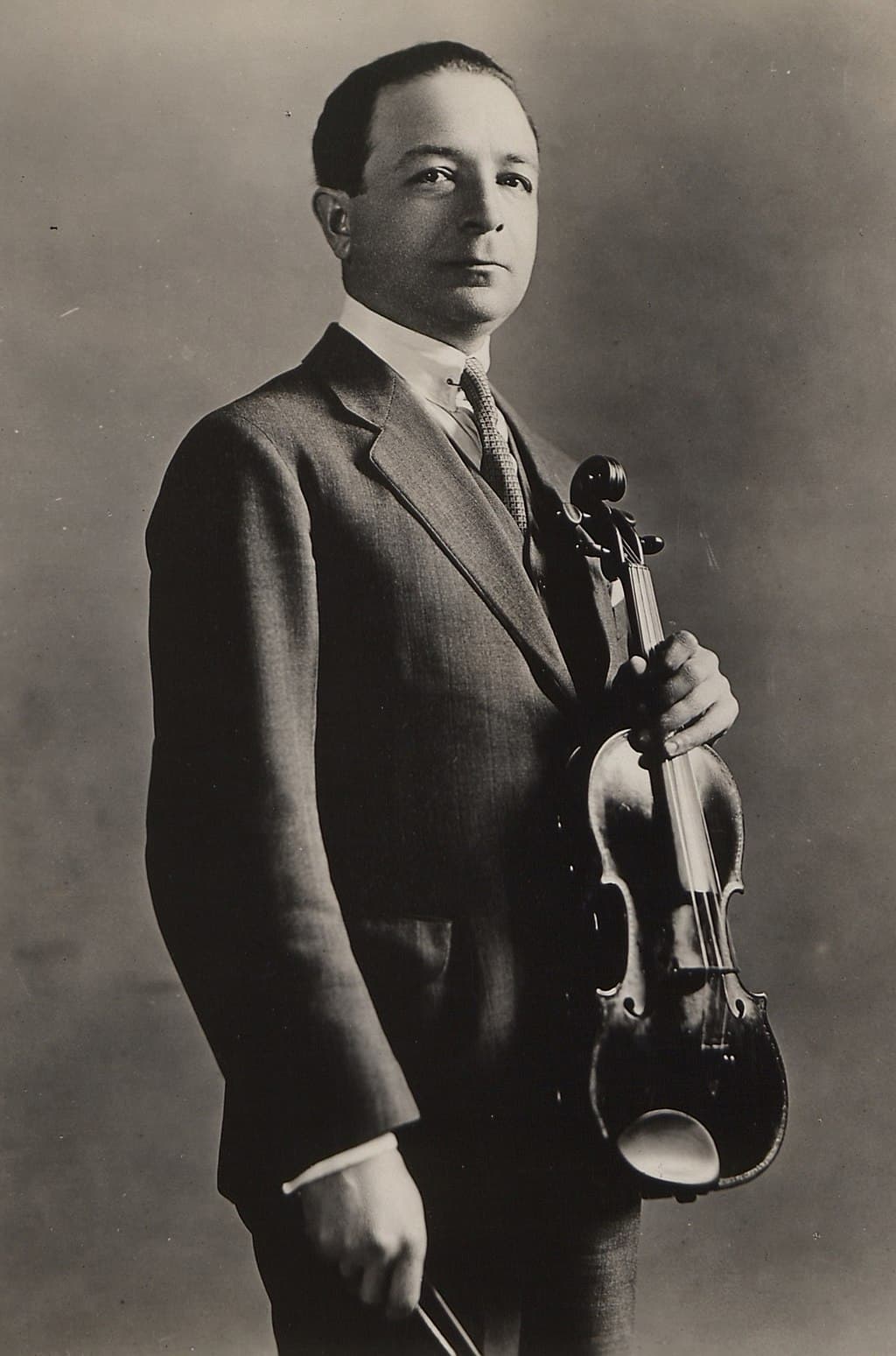

Paweł Kochański © Wikipedia
Happily, Kochański stayed well enough to premiere the work in October 1933 in Warsaw. But his health deteriorated rapidly afterward, and he died a few months later.
Before the score’s publication, Szymanowski edited the dedication to read “A la memoire du Grand Musicien, mon cher et inoubliable Ami, Paweł Kochański” (“In memory of the Great Musician, my dear and unforgettable Friend, Paweł Kochański”).
It ended up being Szymanowski’s last big work, too. He died in 1937 of tuberculosis.
Dmitri Shostakovich: Piano Trio No. 2 (1943-44)
Composer Dmitri Shostakovich began his second piano trio in late 1943 and finished it in August 1944.
While he was working on the trio, in February 1944, a close friend named Ivan Sollertinsky died in his sleep.
Sollertinsky was a brilliant figure who reportedly spoke twenty-six languages (and no, that’s not a typo). Among other things, he helped introduce Mahler‘s music to the Soviet Union.
Understandably, Shostakovich was devastated at the loss, and he wrote that devastating into his haunting piano trio.
According to Sollertinsky’s sister, the trio’s second movement was a portrait of her late brother. It is followed by a tragic dirge.
Arvo Pärt: Für Alina (1976)
There’s a deeply bittersweet real-life story behind Estonian composer Arvo Pärt’s short piano piece Für Alina (or “For Alina”).
In the 1970s, some family friends broke up. The father of the family left for England, and his teenage daughter Alina chose to go with him to see more of the world beyond Estonia.
The work is Pärt comforting his friend, Alina’s mother, while also recognizing her grief at her little girl leaving home.
Conclusion
Classical musicians can certainly be temperamental, but as this overview proves, sometimes the best friendships are friendships based on music!
What are your favorite friendship stories in the history of classical music? What pieces would you add to our list?
Sunday, January 7, 2024
Friday, May 19, 2023
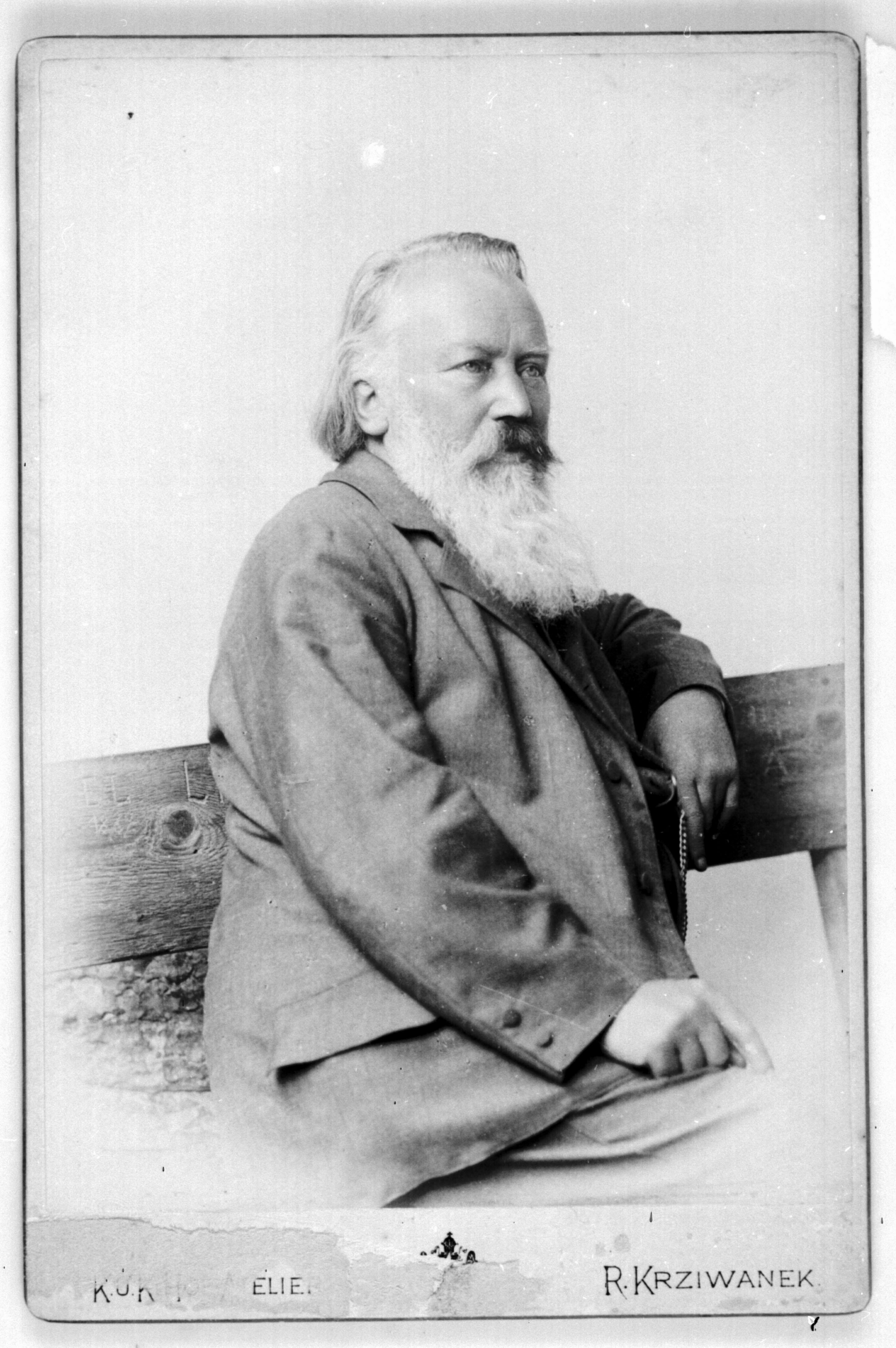
Brahms on the Road: A Trip to Transylvania with Piano and Violin I

Johannes Brahms
In 1879, Brahms wrote to the librarian at the Gesesllschaft der Musikfreunde that he and the violinist Joseph Joachim were planning a tour to the extremes of the Austro-Hungarian Empire. Could he please send him, with the greatest urgency, some music by Beethoven, Schubert, and a bit of Schumann? Please have this in the mail two weeks ago! If the librarian couldn’t get these out of the library, please buy the Peters edition of the individual works requested and if those aren’t available, the complete violin sonatas of Beethoven and Schubert would do. Quickly!
Brahms was taking to the hinterlands with Joachim for a series of concerts. They were travelling deep into the Austro-Hungarian empire, to the middle of current-day Romania, which for the Viennese-living Brahms, would be like a New Yorker venturing into deepest Iowa.
For Brahms, this was a momentous decision: he hadn’t been on the road touring since the late 1860s when he needed the money, and when he was on tour, he complained about what the constant concertizing did to his fingers. Nonetheless, when Joachim’s agent suggested the tour as a way of combining music making with a holiday, Brahms was interested. Now that he was wealthier and could afford the leisure time, he could travel for the pleasure of it.
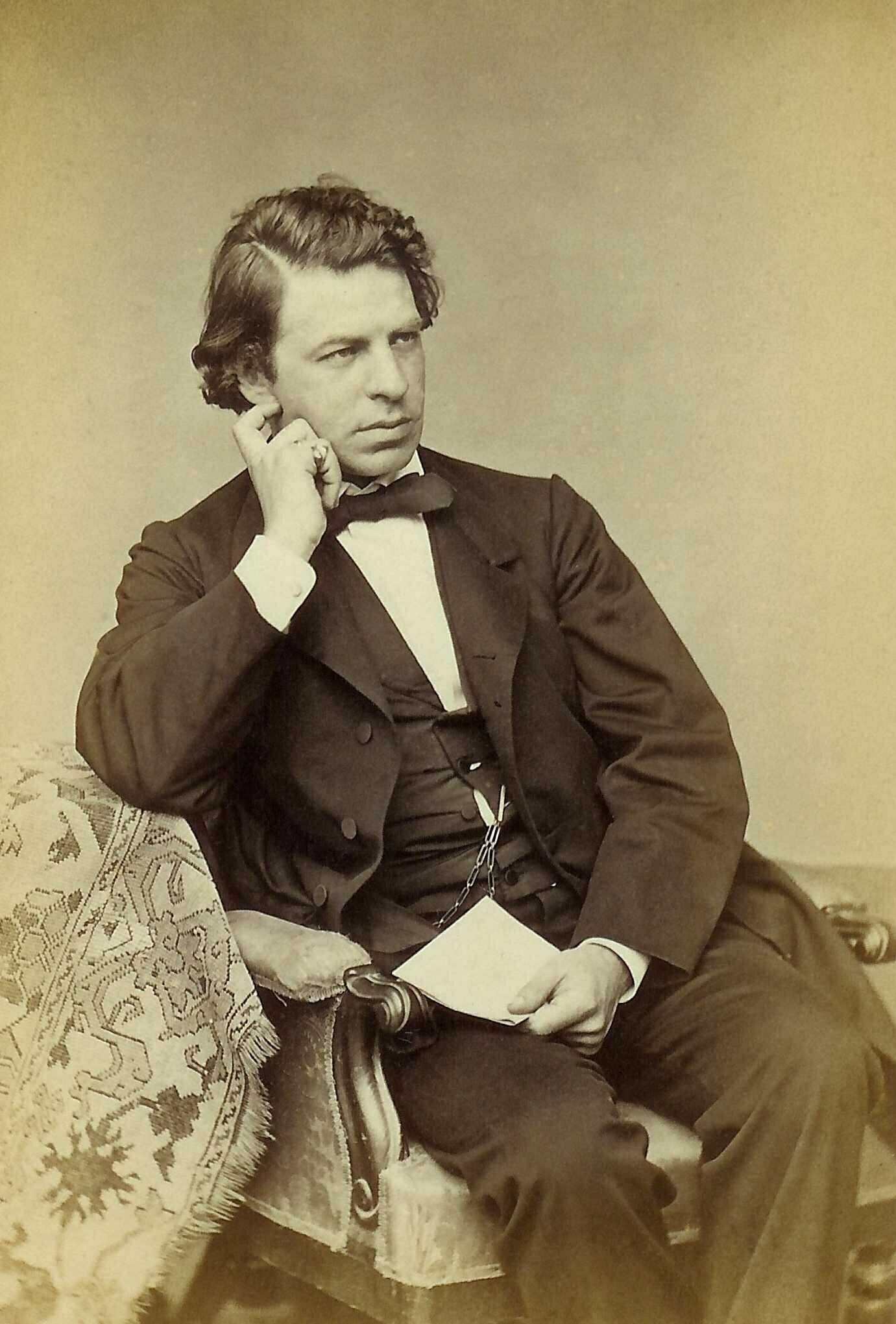

Joseph Joachim
It wasn’t easy to convince Brahms to go. Initially, he was reluctant, writing to his publisher Simrock that ‘…all concert tours…are a dubious pleasure.’ He said he wanted to travel in comfort and do some touring, but his concertizing companions, in the past, only wanted to do more and more concerts, scarcely lifting their eyes from the music to admire the scenery, and make money, of course. Eventually, though, he agreed and the tour was on.
Brahms and Joachim had only one day of rehearsal in Budapest, but then they were playing music that they probably knew from memory, having played it together for past quarter-century, with the one exception of a new work. The repertoire they travelled with included works from Bach to Brahms’ latest new work: the Violin Concerto, Op. 77. Joachim was the dedicatee of the work and had played its premiere, which hadn’t been a success. Joachim wanted to take it on the road as he needed to perform it more but Brahms wasn’t certain about reducing the orchestra to piano accompaniment alone. Joachim brought along Mendelssohn’s Violin Concerto as a backup, reminding Brahms that he had learned it from Mendelssohn himself.
The tour started on 13 September 1879 in Budapest, then by train to the city of Arad, just over the border in modern-day Romania. The next morning, off to Timişoara by carriage for a concert, return that night back to Arad, and then off to Sighişoara by train, concert the next day, and off the following day to Braşov. Back to the carriage for a trip to Sibiu, then onto Cluj, returning by train to Budapest on 24 September. This 11-day trip covered 1,600 km (1,000 miles).
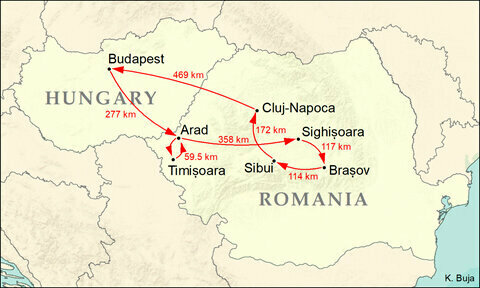
The concert in Arad sold out almost immediately. The programme included Schumman’s Fantasiestücke for Piano and Violin (an arrangement of the Fantasiestücke for clarinet and piano), Tartini’s Devil’s Trill Sonata, and works by Bach, Beethoven, and Brahms.
Arad wasn’t quite as desolate and isolated as Brahms had imagined it to be in this tour of remote regions of the Empire. It was an important transportation hub, had a large military establishment, had the sixth music academy on the continent (opening only 11 years after the Royal Academy in London), and was a bustling commercial centre.
Reviewers noted in particular Brahms’ performance of the Schumann Novelletten, which seems to have been Brahms’ first performance of the entire work ever.
Off by single-track railroad to Timişoara, where the concert was promoted as presenting ‘The Piano Hero and the Violin King.’ The concert started with the Beethoven Violin Sonata, Op. 30, and closed with the Brahms Violin Concerto, Op. 77, arranged for violin and piano.
Finally, Brahms’ Violin Concerto was coming in for praise, with one reviewer calling it ‘one of the most important compositions today,’ but wished for an orchestra to accompany, rather than just a piano. Reports of the concert couldn’t understate their importance to the town: ‘anybody who was anyone, by birth, rank, position, anyone with an understanding for music, was present. They held their breath at the wonderful sounds of the Violin King and the rare virtuosity of Brahms, a pianist of the first rank. Stormy applause followed each number; the audience left highly satisfied, conscious of having been present at an evening of rare artistry.’
