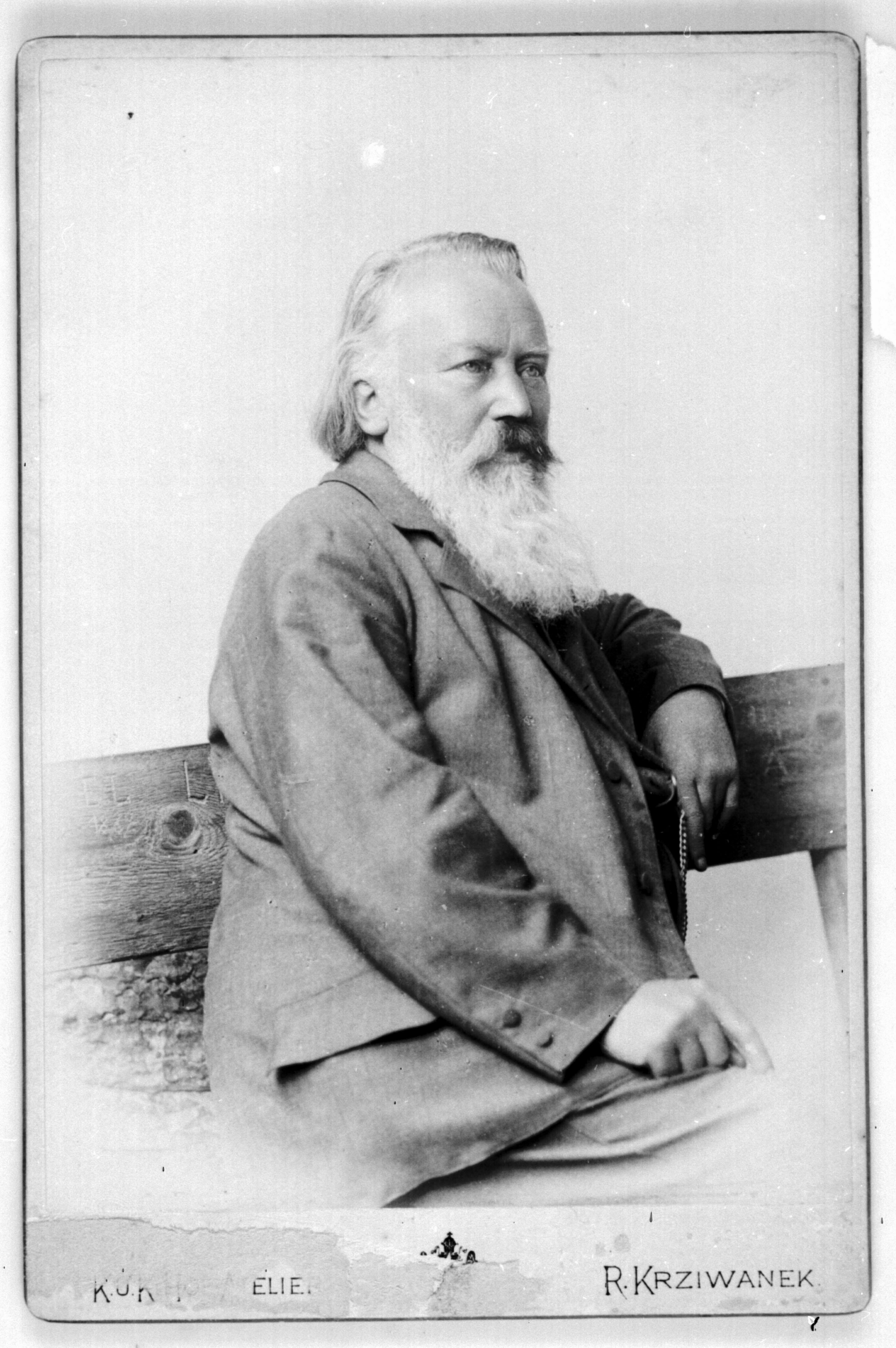

Johannes Brahms
In 1879, Brahms wrote to the librarian at the Gesesllschaft der Musikfreunde that he and the violinist Joseph Joachim were planning a tour to the extremes of the Austro-Hungarian Empire. Could he please send him, with the greatest urgency, some music by Beethoven, Schubert, and a bit of Schumann? Please have this in the mail two weeks ago! If the librarian couldn’t get these out of the library, please buy the Peters edition of the individual works requested and if those aren’t available, the complete violin sonatas of Beethoven and Schubert would do. Quickly!
Brahms was taking to the hinterlands with Joachim for a series of concerts. They were travelling deep into the Austro-Hungarian empire, to the middle of current-day Romania, which for the Viennese-living Brahms, would be like a New Yorker venturing into deepest Iowa.
For Brahms, this was a momentous decision: he hadn’t been on the road touring since the late 1860s when he needed the money, and when he was on tour, he complained about what the constant concertizing did to his fingers. Nonetheless, when Joachim’s agent suggested the tour as a way of combining music making with a holiday, Brahms was interested. Now that he was wealthier and could afford the leisure time, he could travel for the pleasure of it.
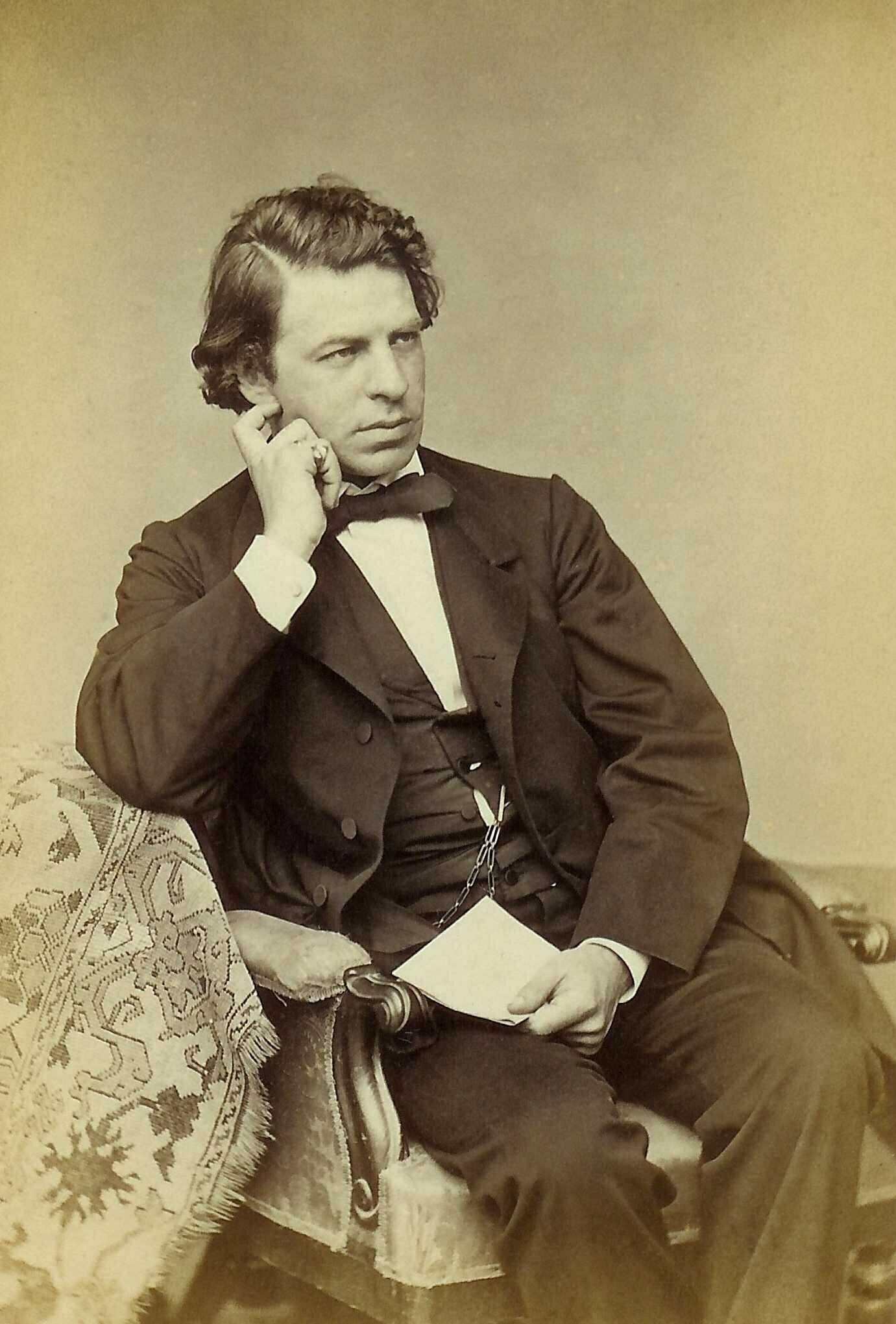

Joseph Joachim
It wasn’t easy to convince Brahms to go. Initially, he was reluctant, writing to his publisher Simrock that ‘…all concert tours…are a dubious pleasure.’ He said he wanted to travel in comfort and do some touring, but his concertizing companions, in the past, only wanted to do more and more concerts, scarcely lifting their eyes from the music to admire the scenery, and make money, of course. Eventually, though, he agreed and the tour was on.
Brahms and Joachim had only one day of rehearsal in Budapest, but then they were playing music that they probably knew from memory, having played it together for past quarter-century, with the one exception of a new work. The repertoire they travelled with included works from Bach to Brahms’ latest new work: the Violin Concerto, Op. 77. Joachim was the dedicatee of the work and had played its premiere, which hadn’t been a success. Joachim wanted to take it on the road as he needed to perform it more but Brahms wasn’t certain about reducing the orchestra to piano accompaniment alone. Joachim brought along Mendelssohn’s Violin Concerto as a backup, reminding Brahms that he had learned it from Mendelssohn himself.
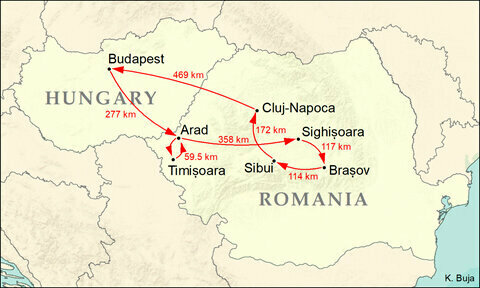
The tour started on 13 September 1879 in Budapest, then by train to the city of Arad, just over the border in modern-day Romania. The next morning, off to Timişoara by carriage for a concert, return that night back to Arad, and then off to Sighişoara by train, concert the next day, and off the following day to Braşov. Back to the carriage for a trip to Sibiu, then onto Cluj, returning by train to Budapest on 24 September. This 11-day trip covered 1,600 km (1,000 miles).
The concert in Arad sold out almost immediately. The programme included Schumman’s Fantasiestücke for Piano and Violin (an arrangement of the Fantasiestücke for clarinet and piano), Tartini’s Devil’s Trill Sonata, and works by Bach, Beethoven, and Brahms.
Arad wasn’t quite as desolate and isolated as Brahms had imagined it to be in this tour of remote regions of the Empire. It was an important transportation hub, had a large military establishment, had the sixth music academy on the continent (opening only 11 years after the Royal Academy in London), and was a bustling commercial centre.
Reviewers noted in particular Brahms’ performance of the Schumann Novelletten, which seems to have been Brahms’ first performance of the entire work ever.
Off by single-track railroad to Timişoara, where the concert was promoted as presenting ‘The Piano Hero and the Violin King.’ The concert started with the Beethoven Violin Sonata, Op. 30, and closed with the Brahms Violin Concerto, Op. 77, arranged for violin and piano.
Finally, Brahms’ Violin Concerto was coming in for praise, with one reviewer calling it ‘one of the most important compositions today,’ but wished for an orchestra to accompany, rather than just a piano. Reports of the concert couldn’t understate their importance to the town: ‘anybody who was anyone, by birth, rank, position, anyone with an understanding for music, was present. They held their breath at the wonderful sounds of the Violin King and the rare virtuosity of Brahms, a pianist of the first rank. Stormy applause followed each number; the audience left highly satisfied, conscious of having been present at an evening of rare artistry.’