It's all about the classical music composers and their works from the last 400 years and much more about music. Hier erfahren Sie alles über die klassischen Komponisten und ihre Meisterwerke der letzten vierhundert Jahre und vieles mehr über Klassische Musik.
Total Pageviews
Friday, May 19, 2023
Brahms on the Road: A Trip to Transylvania with Piano and Violin I
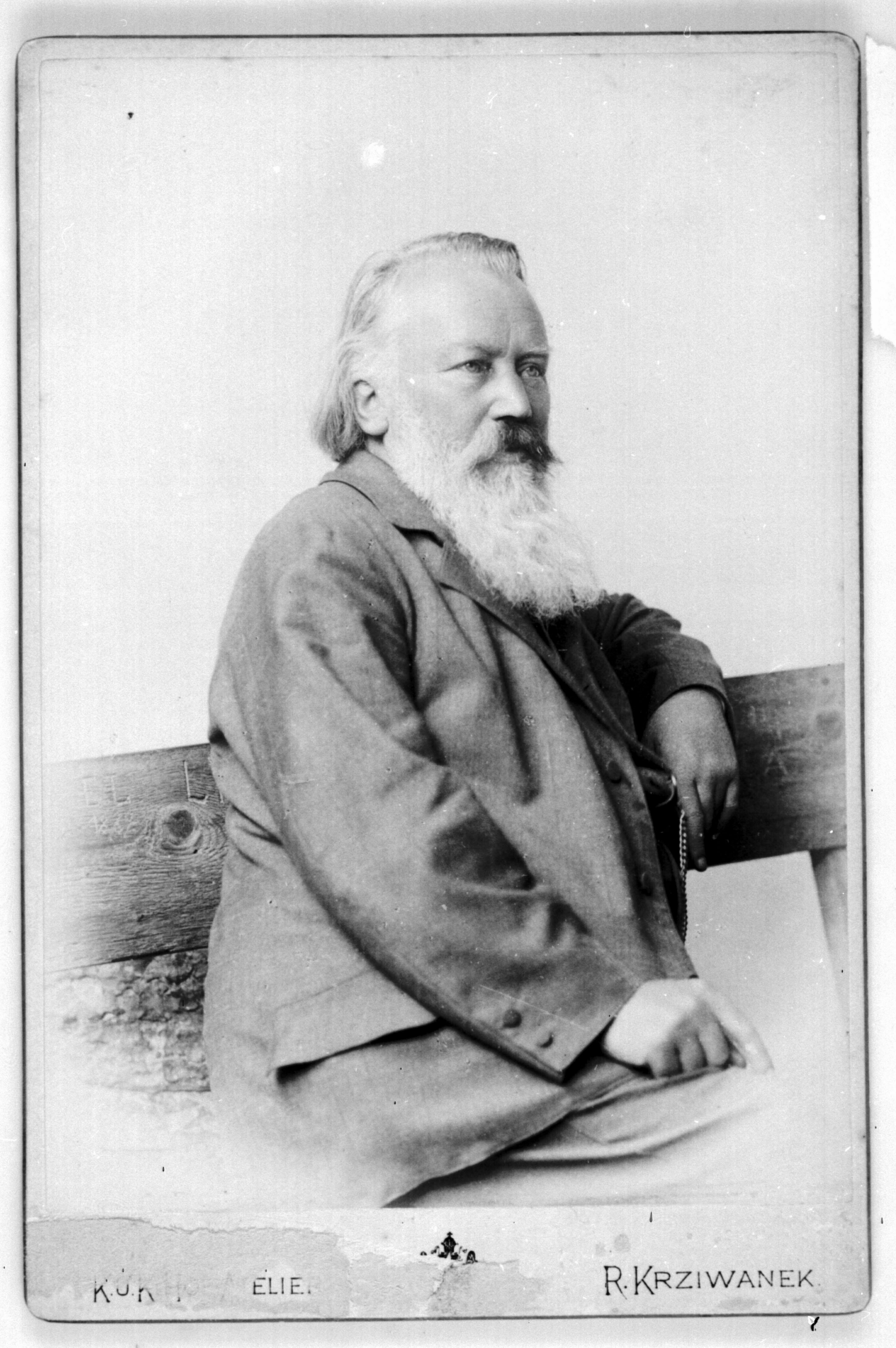

Johannes Brahms
In 1879, Brahms wrote to the librarian at the Gesesllschaft der Musikfreunde that he and the violinist Joseph Joachim were planning a tour to the extremes of the Austro-Hungarian Empire. Could he please send him, with the greatest urgency, some music by Beethoven, Schubert, and a bit of Schumann? Please have this in the mail two weeks ago! If the librarian couldn’t get these out of the library, please buy the Peters edition of the individual works requested and if those aren’t available, the complete violin sonatas of Beethoven and Schubert would do. Quickly!
Brahms was taking to the hinterlands with Joachim for a series of concerts. They were travelling deep into the Austro-Hungarian empire, to the middle of current-day Romania, which for the Viennese-living Brahms, would be like a New Yorker venturing into deepest Iowa.
For Brahms, this was a momentous decision: he hadn’t been on the road touring since the late 1860s when he needed the money, and when he was on tour, he complained about what the constant concertizing did to his fingers. Nonetheless, when Joachim’s agent suggested the tour as a way of combining music making with a holiday, Brahms was interested. Now that he was wealthier and could afford the leisure time, he could travel for the pleasure of it.
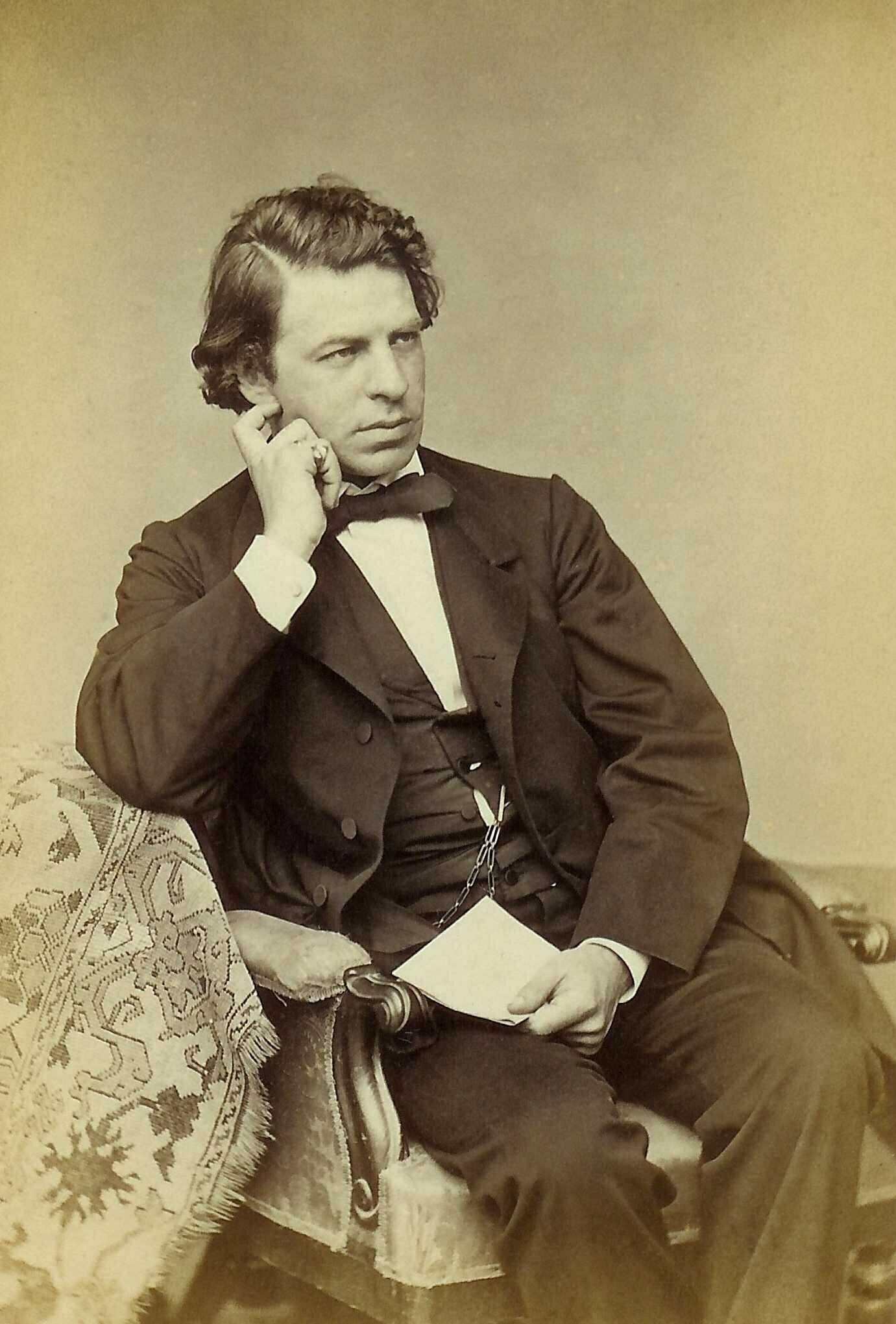

Joseph Joachim
It wasn’t easy to convince Brahms to go. Initially, he was reluctant, writing to his publisher Simrock that ‘…all concert tours…are a dubious pleasure.’ He said he wanted to travel in comfort and do some touring, but his concertizing companions, in the past, only wanted to do more and more concerts, scarcely lifting their eyes from the music to admire the scenery, and make money, of course. Eventually, though, he agreed and the tour was on.
Brahms and Joachim had only one day of rehearsal in Budapest, but then they were playing music that they probably knew from memory, having played it together for past quarter-century, with the one exception of a new work. The repertoire they travelled with included works from Bach to Brahms’ latest new work: the Violin Concerto, Op. 77. Joachim was the dedicatee of the work and had played its premiere, which hadn’t been a success. Joachim wanted to take it on the road as he needed to perform it more but Brahms wasn’t certain about reducing the orchestra to piano accompaniment alone. Joachim brought along Mendelssohn’s Violin Concerto as a backup, reminding Brahms that he had learned it from Mendelssohn himself.
The tour started on 13 September 1879 in Budapest, then by train to the city of Arad, just over the border in modern-day Romania. The next morning, off to Timişoara by carriage for a concert, return that night back to Arad, and then off to Sighişoara by train, concert the next day, and off the following day to Braşov. Back to the carriage for a trip to Sibiu, then onto Cluj, returning by train to Budapest on 24 September. This 11-day trip covered 1,600 km (1,000 miles).
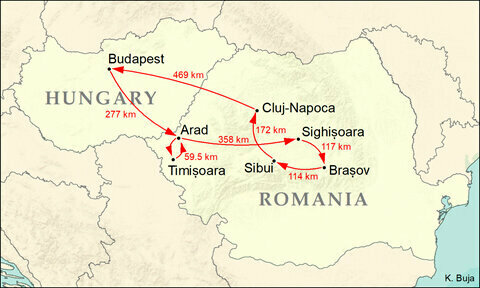
The concert in Arad sold out almost immediately. The programme included Schumman’s Fantasiestücke for Piano and Violin (an arrangement of the Fantasiestücke for clarinet and piano), Tartini’s Devil’s Trill Sonata, and works by Bach, Beethoven, and Brahms.
Arad wasn’t quite as desolate and isolated as Brahms had imagined it to be in this tour of remote regions of the Empire. It was an important transportation hub, had a large military establishment, had the sixth music academy on the continent (opening only 11 years after the Royal Academy in London), and was a bustling commercial centre.
Reviewers noted in particular Brahms’ performance of the Schumann Novelletten, which seems to have been Brahms’ first performance of the entire work ever.
Off by single-track railroad to Timişoara, where the concert was promoted as presenting ‘The Piano Hero and the Violin King.’ The concert started with the Beethoven Violin Sonata, Op. 30, and closed with the Brahms Violin Concerto, Op. 77, arranged for violin and piano.
Finally, Brahms’ Violin Concerto was coming in for praise, with one reviewer calling it ‘one of the most important compositions today,’ but wished for an orchestra to accompany, rather than just a piano. Reports of the concert couldn’t understate their importance to the town: ‘anybody who was anyone, by birth, rank, position, anyone with an understanding for music, was present. They held their breath at the wonderful sounds of the Violin King and the rare virtuosity of Brahms, a pianist of the first rank. Stormy applause followed each number; the audience left highly satisfied, conscious of having been present at an evening of rare artistry.’
Wearing Your Music on Your Gown
by Maureen Buja
The 2023 Met Gala brought out all kinds of dresses, including Karl Lagerfeld’s 40-year-old violin dress, designed in 1983 for Chloé, worn here by Olivia Wilde.
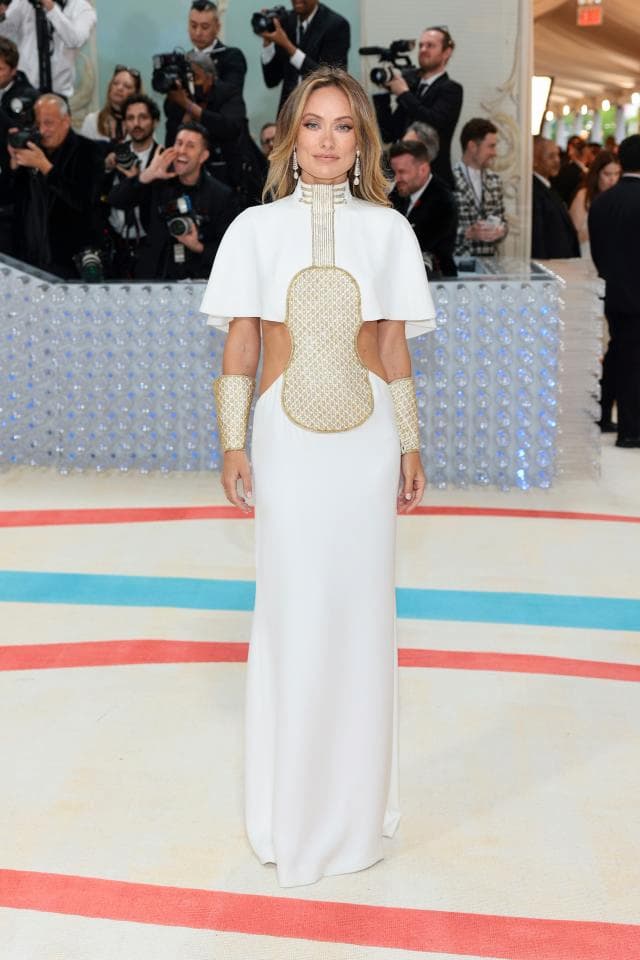

Olivia Wilde in Lagerfeld
But Lagerfeld wasn’t the only designer to find his inspiration in the instruments of music. Viktor and Rolf used pink violins to great effect in 2008.
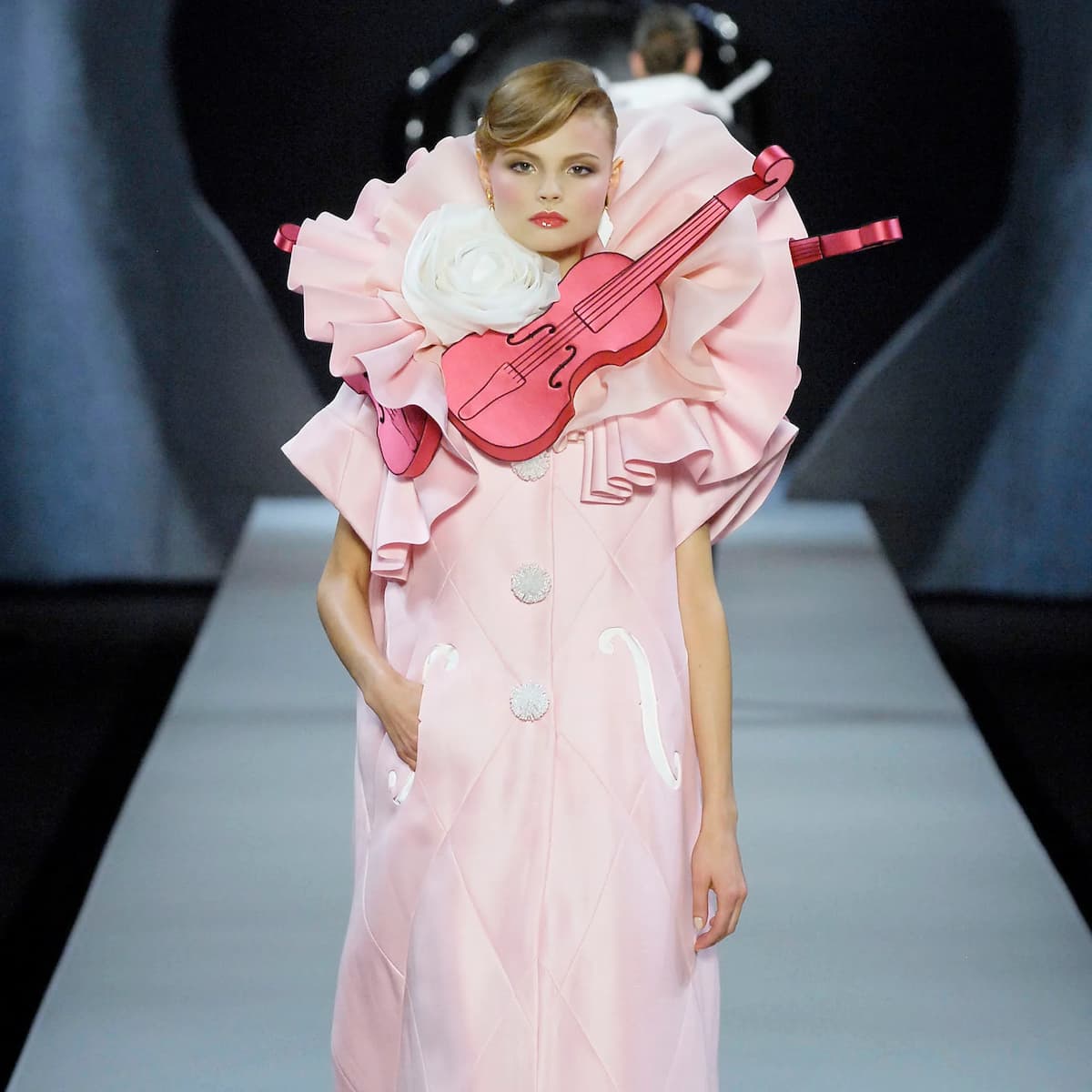

Viktor & Rolf, Spring 2008 Ready-to-Wear (photo by Marcio Madeira)
In fact, if we go back to 1939, we have Elsa Schiaparelli’s music dress in white organza and gloves, embroidered with coloured metallic threads.
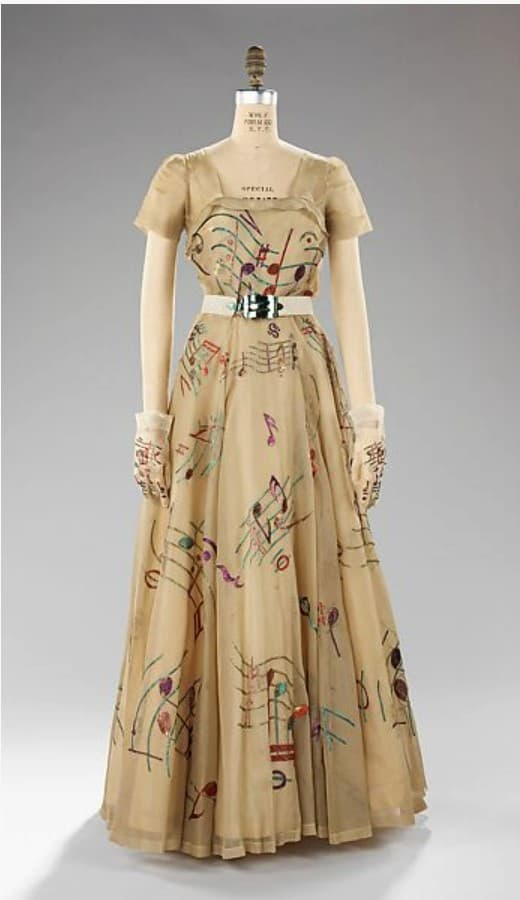

Elsa Schiaparelli, 1939 (Met Museum)
In 1988, Yves Saint Laurent’s Spring collection used Braque’s musical instruments as its inspiration.
Michael G. Cunningham: Free Designs: IV. Georges Braque (Moravian Philharmonic Orchestra; Vit Micka, cond.)
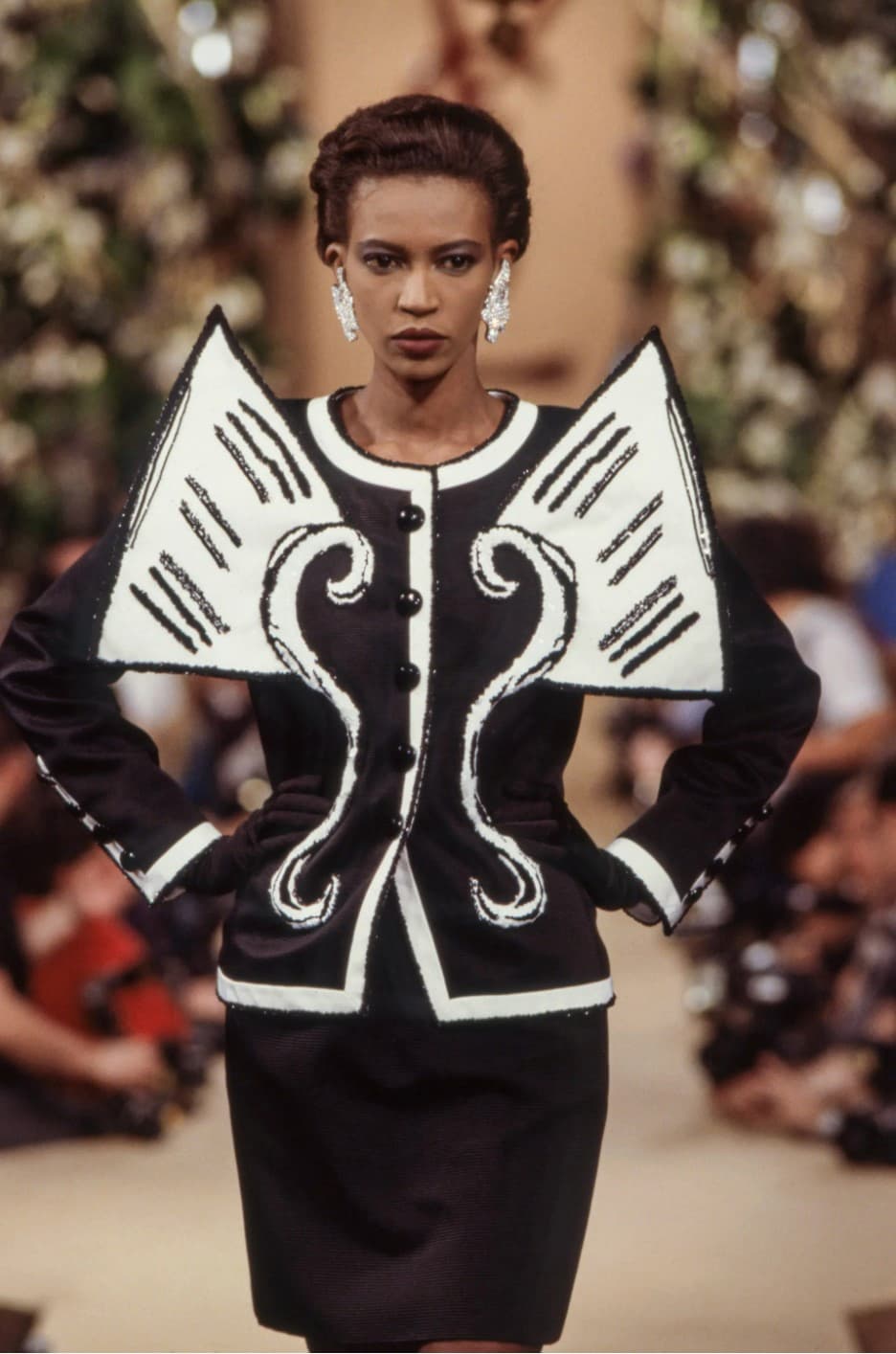

Yves Saint Laurent, Braque, Spring 1988 Couture
In their Fall 2011 Ready-to-Wear collection, Threeasfour used parts of real instruments in their design, such as this violin body.
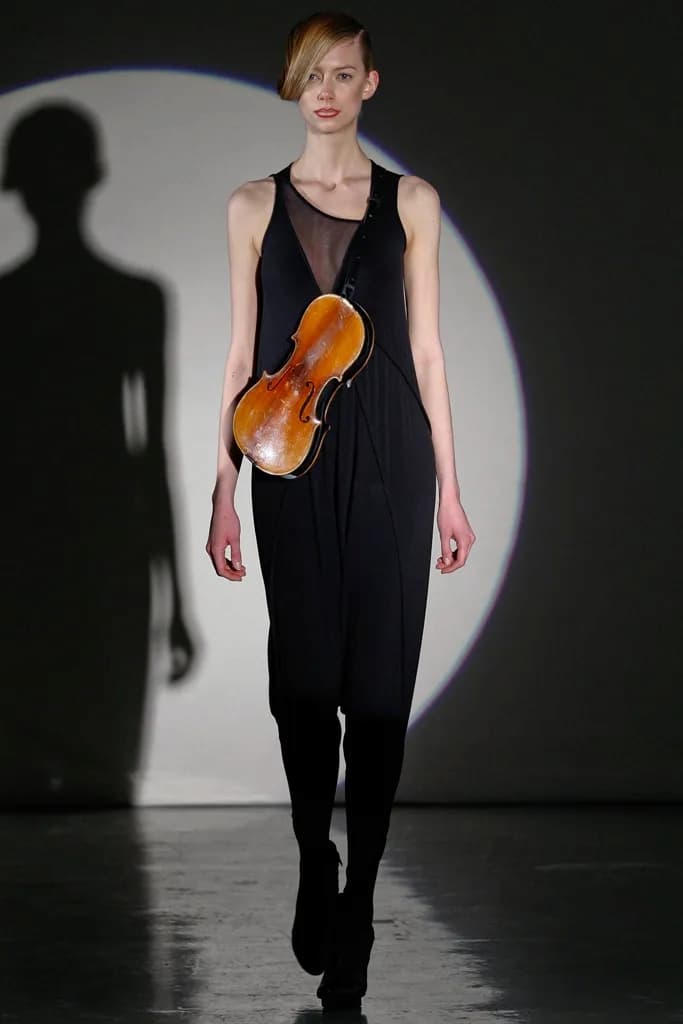

Threeasfour, Fall 2011 Ready-to-Wear, Violin
Maria Grazia Chiuri and Pierpaolo Piccioli created Valentino’s Spring 2014 show completely based on opera, including this dress based on La Traviata that was later worn by Katy Perry to the 2014 GRAMMY Awards.
Giuseppe Verdi: La traviata – Act I: Dell’invito trascorsa e gia l’ora (Rosanna Carteri, Violetta; Rome Opera House Chorus; Rome Opera House Orchestra; Pierre Monteux, cond.)
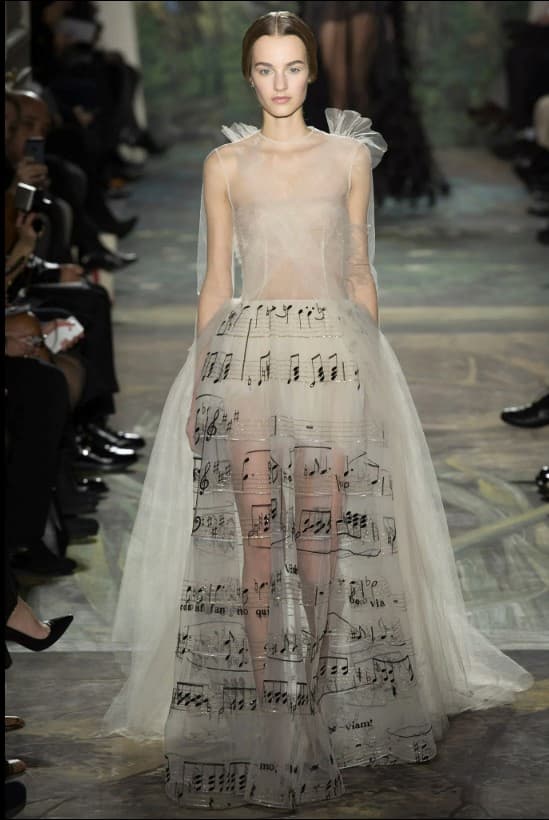

Valentino, La Traviata, Spring 2014 Couture
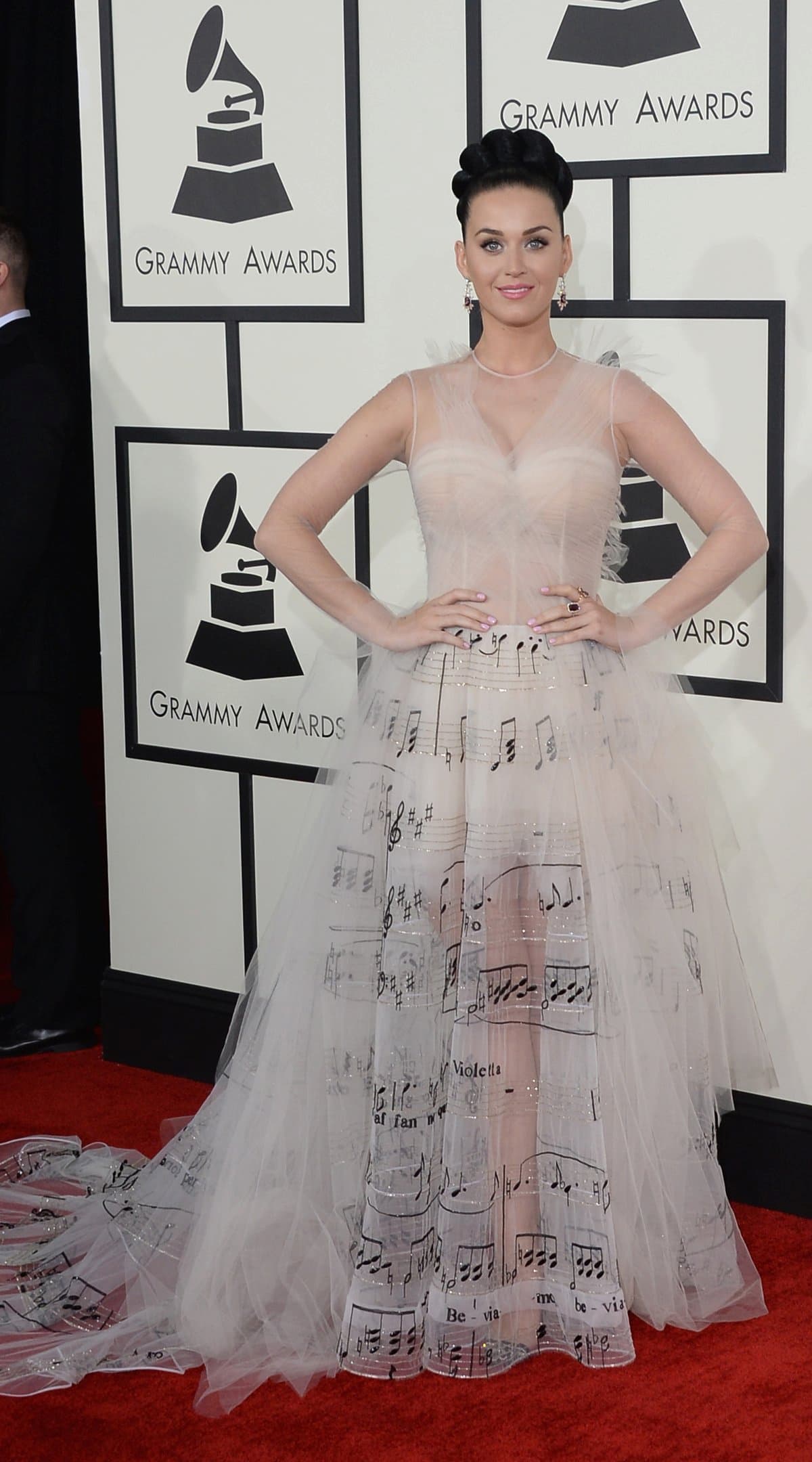

Katy Perry at the 2014 Grammy’s in Valentino
For the Spring 2017 Ready-to-Wear collection, Dolce & Gabbana used the familiar keyboard design for a very short skirt, worn under a highly elaborate jacket.
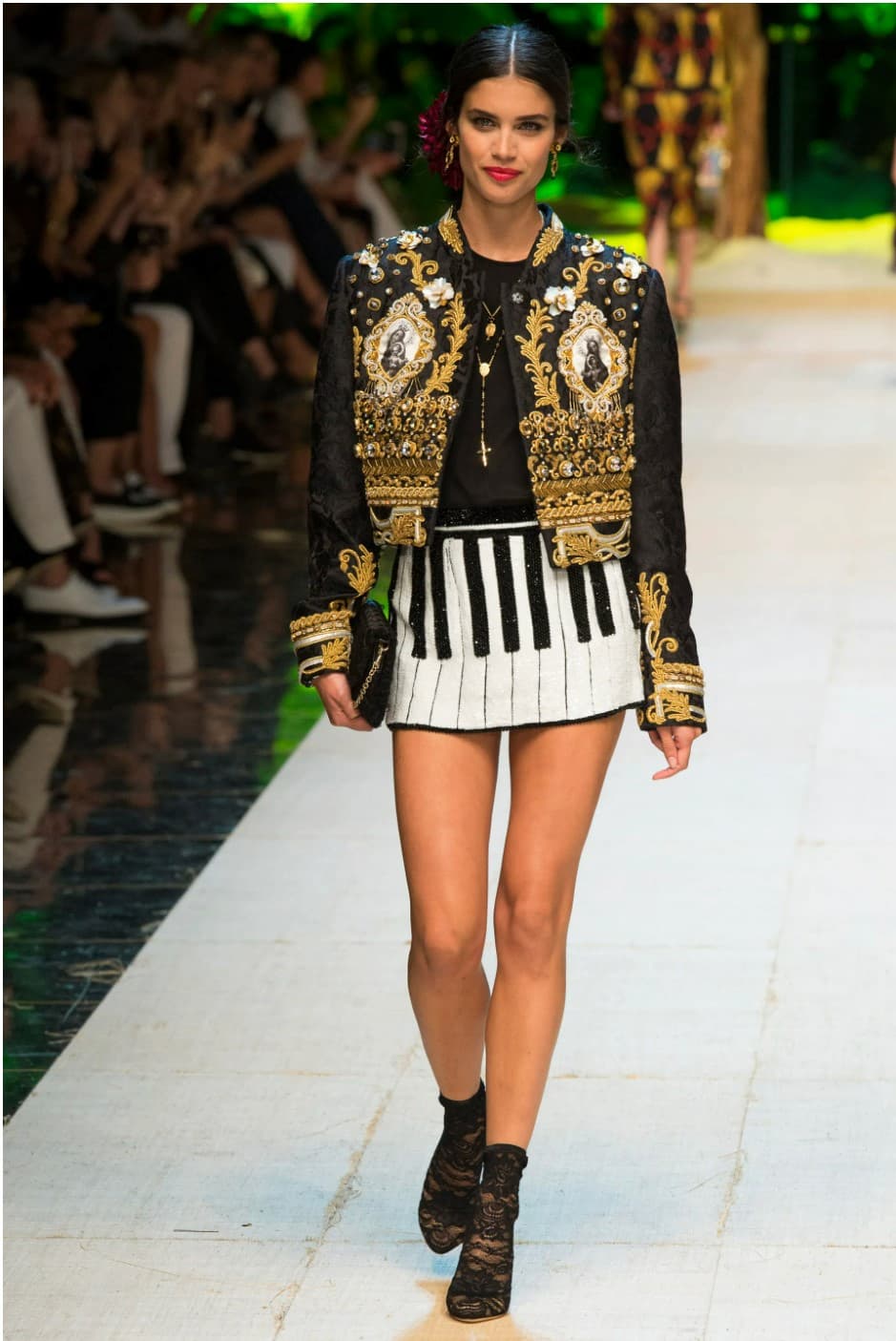

Dolce & Gabbana, Spring 2017 ready-to-wear
For the Spring 2020 catwalks, Jeremy Scott for Moschino also dipped into Braque’s cubist instruments.
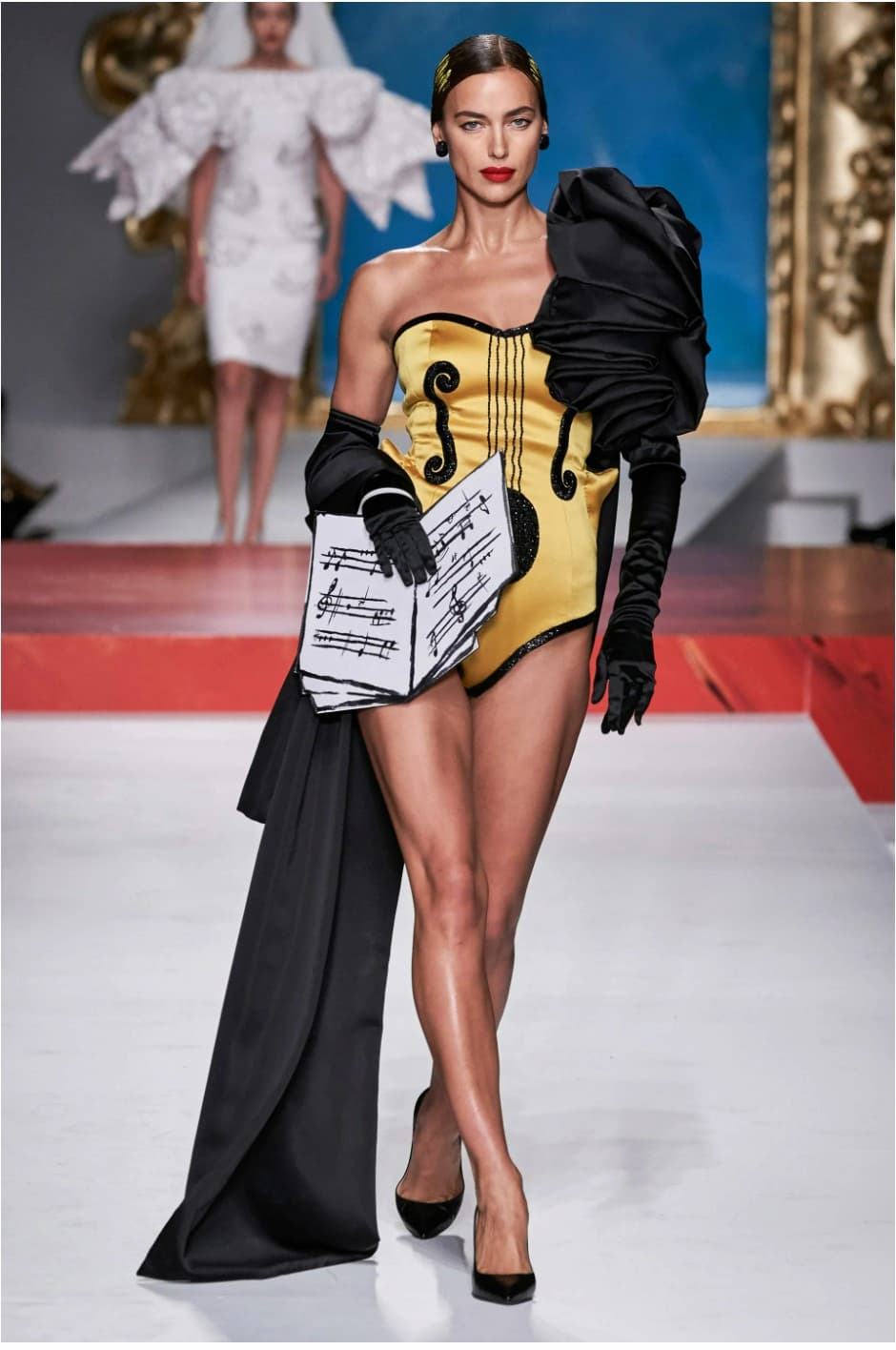

Yellow Violin, Moschino
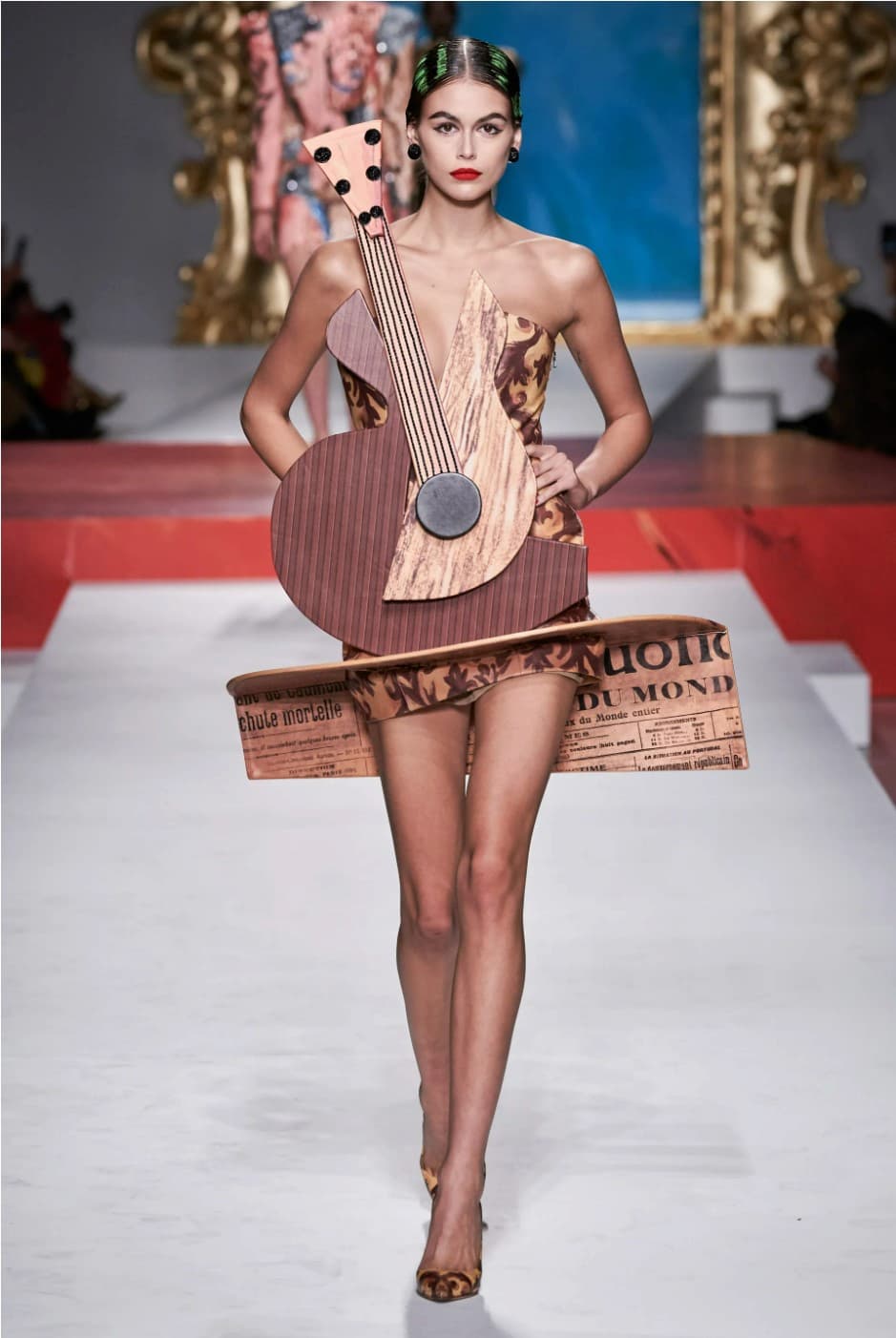

Pink Guitar, Moschino
And Kerby Jean-Raymond for Pyer Moss used not only the familiar piano key pattern but also the shapes of instruments, such as the curve of an electric guitar on a lapel.
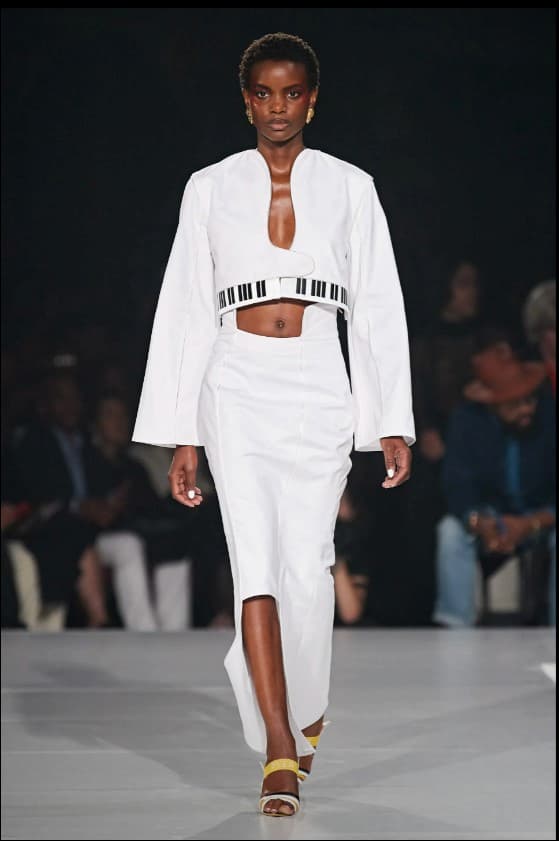

Pyer Moss, Spring 2020, Ready-to-Wear – Piano top
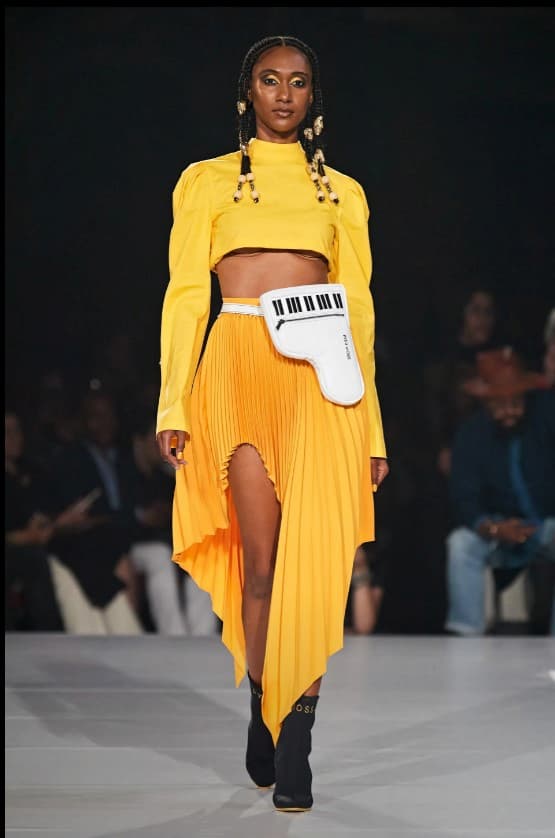

Pyer Moss, Spring 2020, Ready-to-Wear, Piano bag
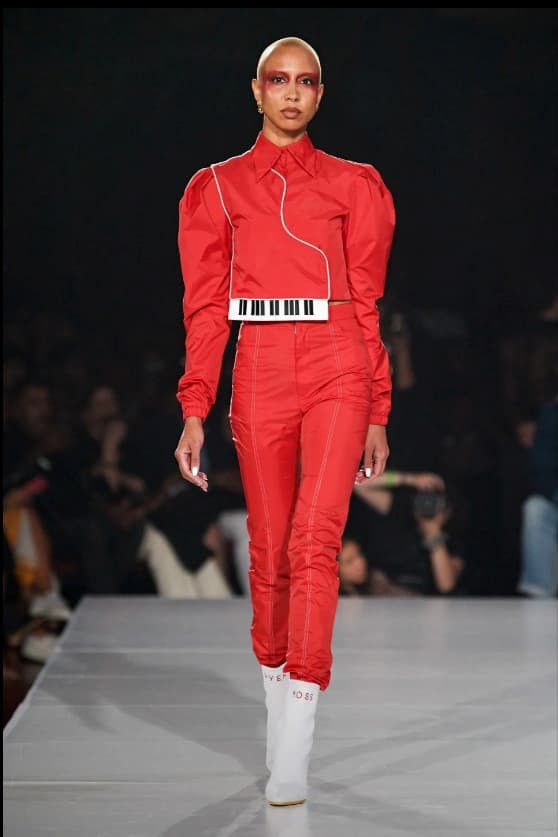

Pyer Moss, Spring 2020, Ready-to-Wear Piano – Red with Keyboard

Pyer Moss, Spring 2020, Ready-to-Wear – Guitar Lapel
If all this is just a bit too high-style, then we can look at the new villain character for next season’s Doctor Who. Played by actor Jinkx Monsoon, the character’s costume not only has a piano keyboard extra- extra-wide lapel but also a piano keyboard lining to her ominous cape.
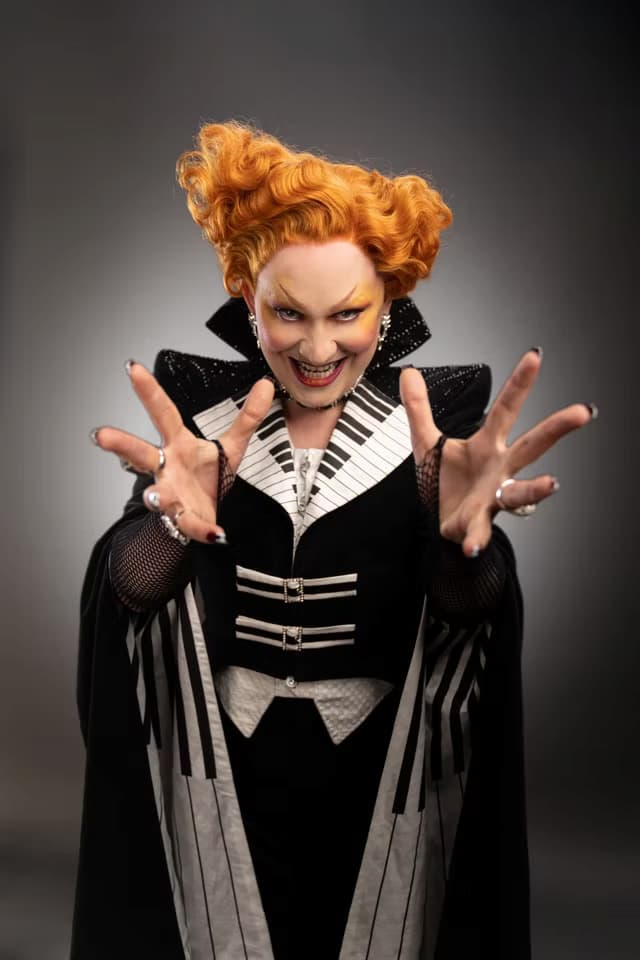

Jinkx Monsoon, 2023
And all of this is just a small part of how music has become part of couture.
Thursday, May 18, 2023
Moody Blues - Nights in White Satin
Catherine, Princess of Wales plays piano in incredible surprise cameo at Eurovision
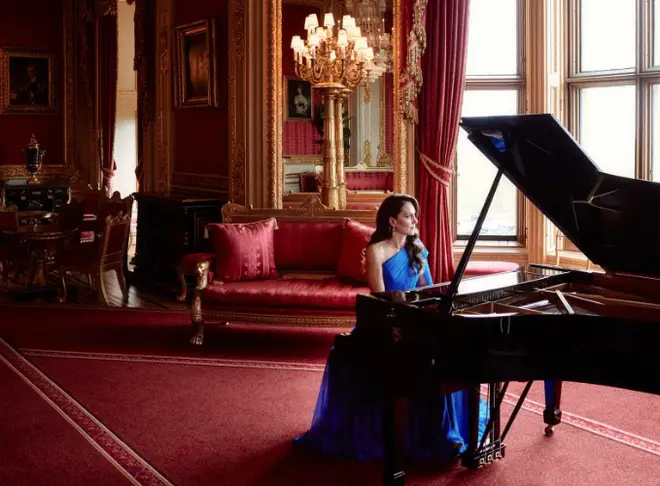

Catherine, Princess of Wales, stunned Eurovision viewers with a surprise cameo appearance playing piano as the song competition finale began.
As is tradition, the grand final of the Eurovision Song Contest 2023 opened with a ‘flag parade’, as performers from the 26 competing countries assembled in the UK’s Liverpool Arena, to a soundtrack of musical performances.
Amongst them: a surprise piano performance from Catherine, Princess of Wales.
This year’s theme was a celebration of Ukraine, as Liverpool hosted the event on behalf of the country since the ongoing Russian invasion made it impossible for last year’s Eurovision winners to do so.
Read more: Catherine, Princess of Wales is a former pianist with a solid grade 5 music theory

Kalush Orchestra - Voices of a New Generation | Grand Final | Eurovision 2023 #UnitedByMusic 🇺🇦🇬🇧
The performance kicked off with 2022 Eurovision winners, Kalush Orchestra, performing ‘Voices of a New Generation’.
The performance blended their winning song ‘Stefania’ with string quartet, a guitar-shredding solo by 2022 runner-up Sam Ryder atop the city’s Royal Liver Building, a ballet performance, and piano cameos from the Princess of Wales and Andrew Lloyd Webber.
Wearing a royal blue dress in a subtle nod to the Ukrainian flag, the Princess of Wales played a short segment on the piano against the rich, red backdrop of Windsor Castle’s Crimson Drawing Room.
The opening segment also featured a piano performance by the great British composer and musical theatre legend, Andrew Lloyd Webber.
Following the broadcast on Saturday 13 May, the Kalush Orchestra released a statement thanking the Princess of Wales for joining their performance.
They also extended an invitation for her to join them on a future tour: “We would definitely like to invite her to tour with us if she would like to pursue a new career in a hip-hop folk band?!” he Princess of Wales’ first public piano appearance was on Christmas Eve in 2021, when she accompanied singer-songwriter Tom Walker in ‘For Those Who Can’t Be Here’ at Westminster Abbey, dedicating the performance to the ‘unsung heroes’ of the Covid-19 pandemic.
The Princess learned piano as a young girl, taking lessons with Daniel Nicholls between the ages of 10 and 13. She is also known to have achieved Grade 5 in singing and music theory, having reportedly been deputy head chorister in her chapel choir, as well as having played flute in a chamber orchestra and flute choir, alongside her sister Pippa.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)


