It's all about the classical music composers and their works from the last 400 years and much more about music. Hier erfahren Sie alles über die klassischen Komponisten und ihre Meisterwerke der letzten vierhundert Jahre und vieles mehr über Klassische Musik.
Popular Posts
-
by Hermione Lai It’s not really common knowledge, but Georges Bizet was an absolutely brilliant pianist. He entered the class of Antoin...
-
by M aureen Buja With its full title, La mer, trois esquisses symphoniques pour orchestre (The sea, three symphonic sketches for orchest...
-
By Georg Predota “Blind Tom,” as he was generally known, was born into slavery in Columbus, Georgia in 1848. He was sold with his family du...
-
by Emily E. Hogstad June 7th, 2025 The great composers left behind more than just great music: they also left behind advice for their fe...
-
774,844 views May 29, 2024 #pierobarone #ignazioboschetto #tuttiperuno Social • Instagram: @ignazioboschetto.italy • Tiktok: @ignazi...
-
24,755 views Mar 23, 2017 Mozart - Piano Concerto No. 18 in B-flat major, K. 456 Rachmaninov Hall Of Moscow Conservatory Moscow Youth Cham...
-
Join the cast of Les Misérables' 25th anniversary concert as we take a look at the first & last songs from the live musical with our...
-
by Bruce Robinson Be forewarned: Three is an excellent score Recently, I heard a superb premiere of music by an 87-year-old composer. I wo...
-
530,100 views May 30, 2025 In the heart of Paris, dozens of singers and musicians came together to share a powerful message of peace and u...
Übersetzerdienste - Translation Services
Übersetzerdienste - Translation Services
Even after retiring as German Consul, I am still accredited as a German translator and interpreter for the German, Swiss and Austrian Embassy as well as for Regional Trial Court Davao City and all courts nationwide. Please pm for via doringklaus@gmail.com further information. I'll be answering your messages as soon as possible. Please be patient. Auch nach meiner Pensionierung als deutscher Konsul bin ich weiterhin als deutscher Übersetzer und Dolmetscher für die deutsche, schweizerische und österreichische Botschaft sowie für das Regional Trial Court Davao City landesweit akkreditiert. Für weitere Informationen senden Sie bitte eine PN an doringklaus@gmail.com. Ich werde Ihre Nachrichten so schnell wie möglich beantworten.
Total Pageviews
Tuesday, August 29, 2023
Monday, August 28, 2023
Pianist in tears!!!. Most moving piano performance.
IF I NEVER SING ANOTHER SONG by Matt Monro (with lyrics)
"If I Never Sing Another Song" is a song recorded and released by The Man With the Golden Voice, Matt Monro, in 1977.
Sunday, August 27, 2023
Fauré: 15 facts about the Great Composer
Gabriel Fauré (1845–1924) was one of the most influential of French composers, linking the end of Romanticism with the beginnings of the modern era. His Requiem and Pavane remain among the best-loved classical pieces.

1. Happiness is a harmonium
Born in Pamiers in the south of France, Fauré's musical talent became apparent when he was a boy. "I grew up, a rather quiet well-behaved child, in an area of great beauty," he said. "But the only thing I remember really clearly is the harmonium in that little chapel. Every time I could get away I ran there...I played atrociously...but I do remember that I was happy; and if that is what it means to have a vocation, then it is a very pleasant thing."

2. Meeting Saint-Saëns
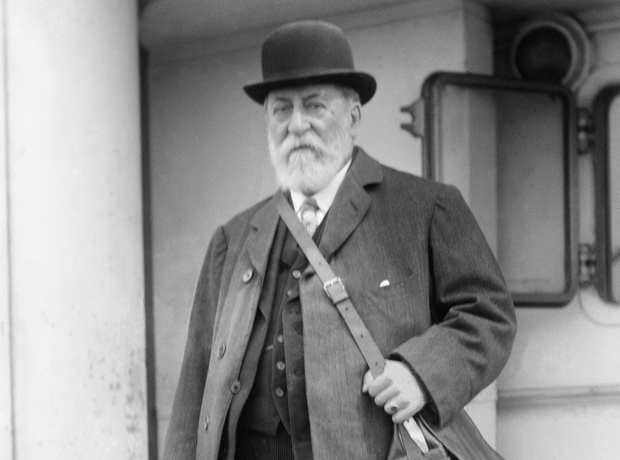
At nine, young Gabriel was sent to Paris to study to become a church organist and choirmaster. A few years later, Saint-Saëns (pictured) took charge of piano studies and introduced contemporary music into the college, including works by Schumann, Liszt and Wagner. Saint-Saëns took a great interest in Fauré's progress and a lifelong friendship was born.
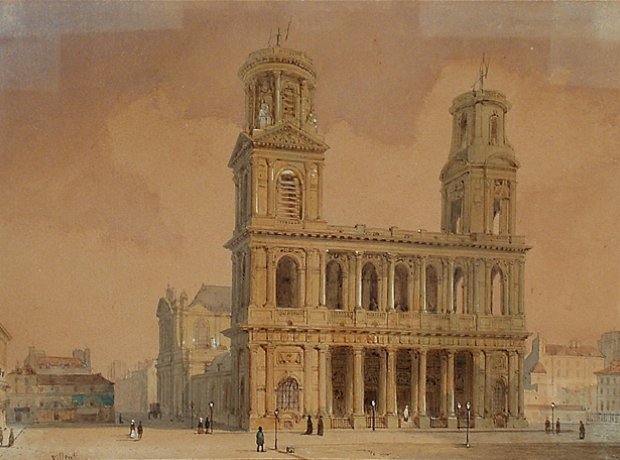
3. Master organist
After graduating in 1865, Fauré earned a modest living as an organist and piano teacher. In October 1871, he was appointed choirmaster at the Église Saint-Sulpice, Paris (pictured), under the organist Widor. During some services, the two improvised simultaneously on the church's two organs, trying to catch each other out with sudden changes of key.

4. Gabriel Faure
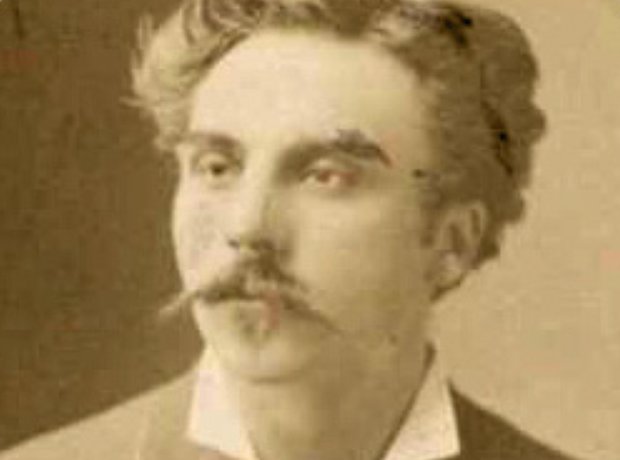
Fauré became a founding member of the Société Nationale de Musique, formed in February 1871 to promote new French music. Other members included Saint-Saëns, Bizet, Chabrier, Franck and Massenet. Many of Fauré's works were first presented at the Society's concerts.

5. A budding composer
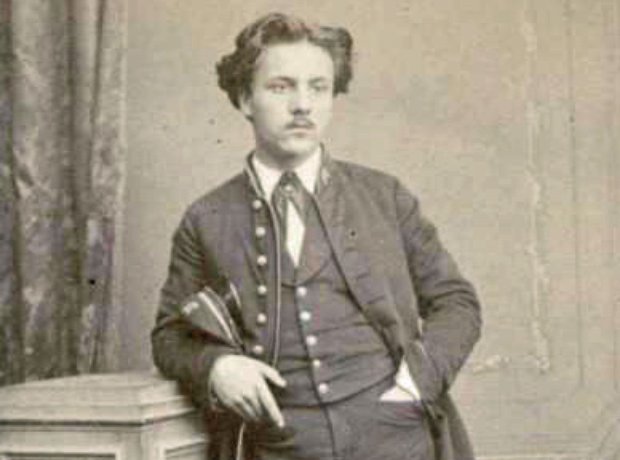
In January 1877, Fauré - aged 31 - had his first violin sonata performed at a Société Nationale concert with great success. It marked a turning-point in his composing career.
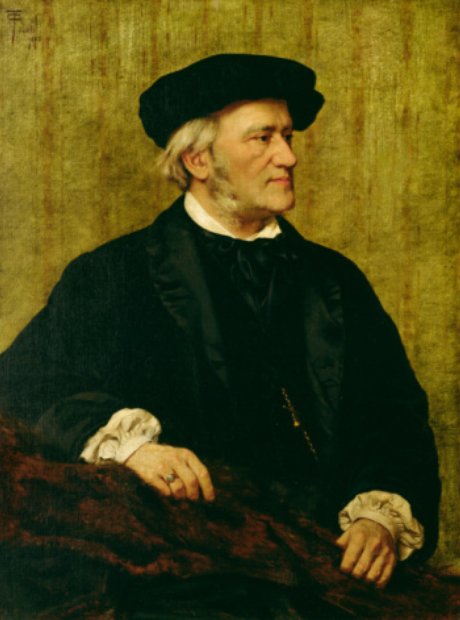

6. Love of Wagner
Fauré greatly enjoyed foreign travel. From 1878, he made trips abroad to see the operas of Wagner (pictured). He saw the complete Ring Cycle in Munich and in London and Die Meistersinger and Parsifal at Bayreuth. Fauré admired Wagner and had a detailed knowledge of his music, but he was one of the few composers of his generation not to be influenced musically by Wagner.

7. Summer retreat
Holding an important post as organist as well as being director of the Paris Conservatoire meant that Fauré had to retreat to the countryside in the summer to concentrate on composing. He began his Requiem in 1887, revised and expanded it over the years, until its final version dating from 1901.

8. Fauré's Requiem
Fauré said of his Requiem, "Everything I managed to entertain by way of religious illusion I put into my Requiem, which moreover is dominated from beginning to end by a very human feeling of faith in eternal rest." Fauré saw death as a "happy deliverance, an aspiration towards happiness above, rather than as a painful experience."
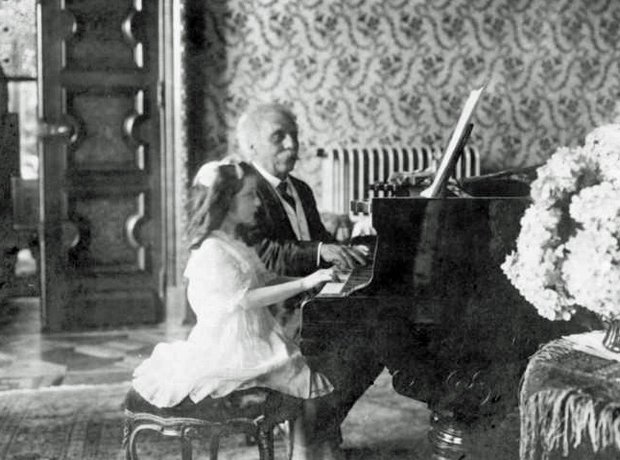

9. Fauré and the Dolly Suite
In his late 40s, the married Fauré fell in love with Emma Bardac. The affair inspired a burst of creativity and a new originality in his music. Fauré wrote the Dolly Suite for piano duet between 1894 and 1897 and dedicated it to Bardac's daughter Hélène, known as "Dolly". Some people suspected that Fauré was Dolly's father.
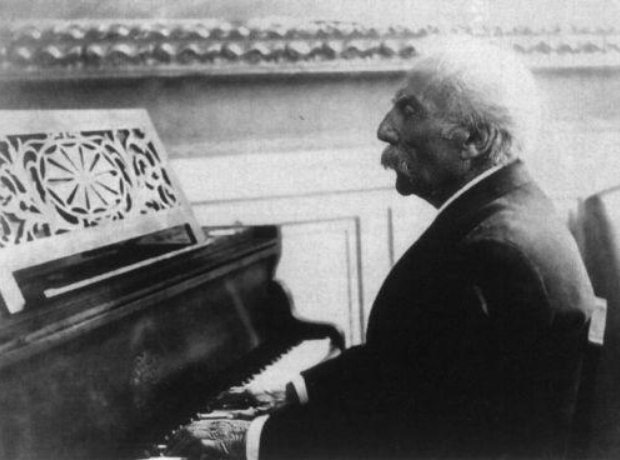

10. Pavane
Fauré's popular Pavane was written for piano and choir in the late 1880s. He described it as "elegant, but not otherwise important," intending it to be played more briskly than it has generally come to be performed. The choral lyrics were based on verses about the romantic helplessness of man.
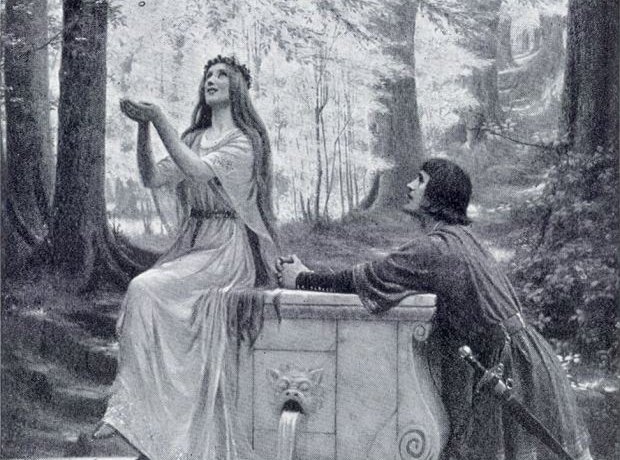

11. Pelléas et Mélisande
Fauré's works of the last years of the 19th century included incidental music for the English premiere of Maurice Maeterlinck's Pelléas et Mélisande, a Symbolist play about forbidden love. The work was very popular and also inspired an opera by Debussy, and incidental music by Arnold Schoenberg and Jean Sibelius.
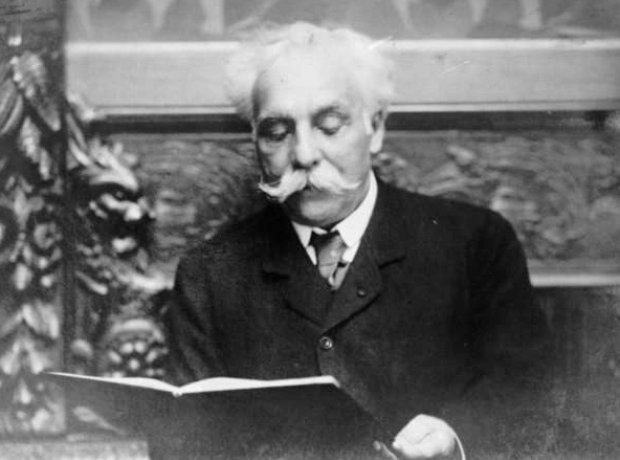

12. The not-very-critical critic
From 1903 to 1921, Fauré regularly wrote music criticism for the newspaper Le Figaro, a role in which he was not at ease. It's thought that Fauré's natural kindness and broad-mindedness meant he tended to emphasise the positive aspects of a work and not be critical enough.
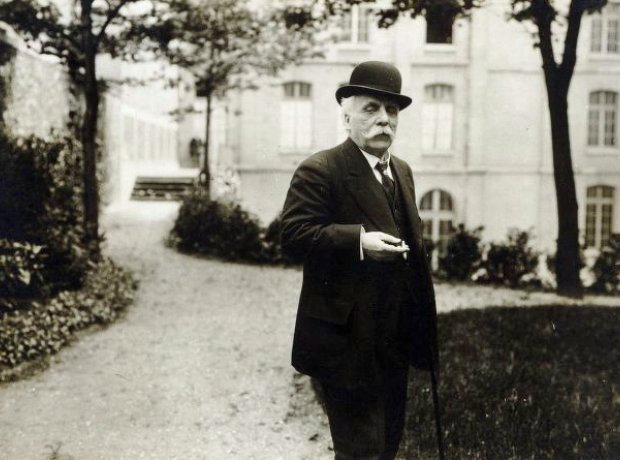

13. Admired by Elgar
Fauré was hugely popular in Britain. He visited often and even played at Buckingham Palace in 1908. He attended the London premiere of Elgar's First Symphony that year and had dinner with Elgar afterwards. "I admired him greatly," said Elgar, who tried to get Fauré's Requiem put on at the Three Choirs Festival.
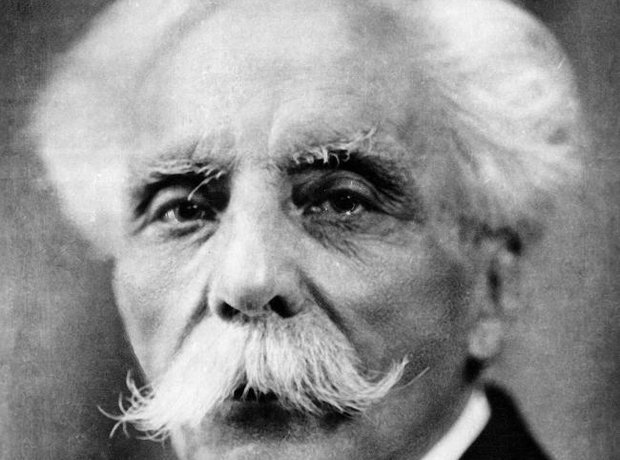

14. Honoured by the state
By his last years, Fauré was recognised in France as the leading French composer of his day. In 1920, at the age of 75, he received the Grand-Croix of the Légion d'Honneur, a rare honour for a musician.
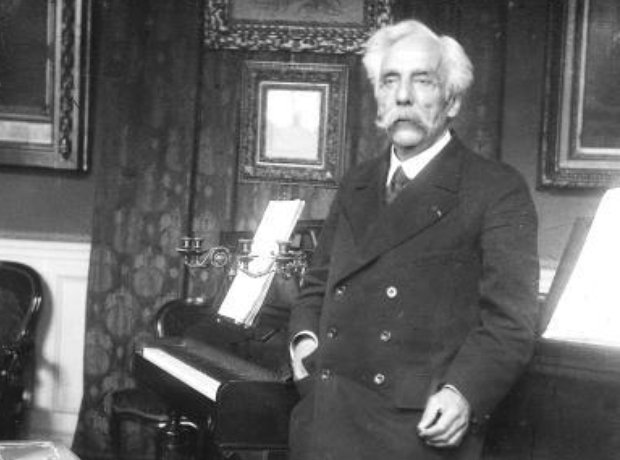

15. Final years
Fauré suffered from poor health in his later years, brought on by heavy smoking. Despite this, he remained available to teach and dispense advice to young composers, including members of Les Six, most of whom were devoted to him. He died in Paris from pneumonia on 4 November 1924 at the age of 79.
Saturday, August 26, 2023
Boney M. - Rivers of Babylon (Sopot Festival 1979)
Friday, August 25, 2023
Vanessa Williams - Save The Best For Last (Official Music Video)
THRILLMAKER: The Humperdinck is back!
BY JOEE GUILAS
AT A GLANCE
This September, thelegendary British crooner returnsto the country as part of hisongoing world tour, “The Legend Continues.” Fans will be serenaded by his passionate performances in a two-night concert at the Newport Performing Arts Theater, Newport World Resorts, Pasay City, on Sept. 9 and 10, 7:30 PM.

Ironic as it may sound, the singer who immortalized the song “Release Me” is not considering releasing his tight hold on fame anytime soon. Legendary balladeer and frequent Manila visitor Engelbert Humperdinck will soon be en route to another world tour, including a stop in the Philippines this September.
“It’s been four years since my last visit, and I’m looking forward to coming over. I’m excited about coming over there. I know that Filipinos love my music. I’ve been spending a lot of time online, and I see them singing my songs on karaoke,” shared Humperdinck. He said this also prompts him to always have something special for his Filipino fans whenever he is afforded the chance to visit the country. This next visit is undoubtedly not going to be an exception.
“I have a surprise for the Filipino people when I get there,” he teased.
The promised surprise is on top of the 87-year-old singer’s new album, "All About Love.” He hopes that some cuts in this new project will be hits just like his classic “Release Me,” which stayed on top of the charts for 56 consecutive weeks in multiple countries.
“The music that I record seems timeless when I recorded them in the past, and I never get tired singing them, especially Release Me,” Humperdinck acknowledged.
Asked whether or not he is getting tired of singing at his ripe age, Humperdinck stressed that slowing down anytime soon is far-fetched, at least at this point: “Retiring is not a word that I use. I have such a great following that I don’t want to disappoint them. Wherever I go, I get such a great reception.” More than this, however, the debt of gratitude to his craft makes him stick to the life of being a musician.
“Music has been my passport to the world. It’s made me see countries I’ve never seen before. It’s a wonderful way to make a living.”
This September, the legendary British crooner returns to the country as part of his ongoing world tour, “The Legend Continues.” Fans will be serenaded by his passionate performances in a two-night concert at the Newport Performing Arts Theater, Newport World Resorts, Pasay City, on Sept. 9 and 10, 7:30 PM.
For over 50 years, Humperdinck mastered wooing audiences worldwide, earning him the title “King of Romance.” Among his commercially successful singles are “Release Me,” “Quando Quando Quando,” “Spanish Eyes,” and many more.
While his captivating vocals have charmed millions of fans, the man earned his icon status in the music industry with massive achievements through the decades. Humperdinck rose in the music scene in the 1960s alongside iconic bands The Beatles and The Rolling Stones. Throughout his long career, he became a four-time Grammy nominee and released dozens of studio albums, selling over 150 million records. To this day, he consistently showcases his legacy and wins the hearts of listeners across the globe.
Now, given all these tucked into his belt, it should be no wonder why fans are finding it difficult to release his music from their playlists.

Ironic as it may sound, the singer who immortalized the song “Release Me” is not considering releasing his tight hold on fame anytime soon. Legendary balladeer and frequent Manila visitor Engelbert Humperdinck will soon be en route to another world tour, including a stop in the Philippines this September.
“It’s been four years since my last visit, and I’m looking forward to coming over. I’m excited about coming over there. I know that Filipinos love my music. I’ve been spending a lot of time online, and I see them singing my songs on karaoke,” shared Humperdinck. He said this also prompts him to always have something special for his Filipino fans whenever he is afforded the chance to visit the country. This next visit is undoubtedly not going to be an exception.
“I have a surprise for the Filipino people when I get there,” he teased.
The promised surprise is on top of the 87-year-old singer’s new album, "All About Love.” He hopes that some cuts in this new project will be hits just like his classic “Release Me,” which stayed on top of the charts for 56 consecutive weeks in multiple countries.
“The music that I record seems timeless when I recorded them in the past, and I never get tired singing them, especially Release Me,” Humperdinck acknowledged.
Asked whether or not he is getting tired of singing at his ripe age, Humperdinck stressed that slowing down anytime soon is far-fetched, at least at this point: “Retiring is not a word that I use. I have such a great following that I don’t want to disappoint them. Wherever I go, I get such a great reception.” More than this, however, the debt of gratitude to his craft makes him stick to the life of being a musician.
“Music has been my passport to the world. It’s made me see countries I’ve never seen before. It’s a wonderful way to make a living.”
This September, the legendary British crooner returns to the country as part of his ongoing world tour, “The Legend Continues.” Fans will be serenaded by his passionate performances in a two-night concert at the Newport Performing Arts Theater, Newport World Resorts, Pasay City, on Sept. 9 and 10, 7:30 PM.
For over 50 years, Humperdinck mastered wooing audiences worldwide, earning him the title “King of Romance.” Among his commercially successful singles are “Release Me,” “Quando Quando Quando,” “Spanish Eyes,” and many more.
While his captivating vocals have charmed millions of fans, the man earned his icon status in the music industry with massive achievements through the decades. Humperdinck rose in the music scene in the 1960s alongside iconic bands The Beatles and The Rolling Stones. Throughout his long career, he became a four-time Grammy nominee and released dozens of studio albums, selling over 150 million records. To this day, he consistently showcases his legacy and wins the hearts of listeners across the globe.
Now, given all these tucked into his belt, it should be no wonder why fans are finding it difficult to release his music from their playlists.
The Child Prodigies of Classical Music
From Hummel to Beethoven
By Georg Predota, Interlude
In historical studies of music, compositions by children have generally not been held in high regard. The one exception, of course, is Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart, “commonly regarded as the child composer par excellence.” While the focus has so far been on childhood works by major composers, a recent publication by Barry Cooper has suggested, “that we might well look at the major works of all child composers regardless how they developed in later life.” And while it is easy to imagine a child composer writing a short song or piano piece, I was particularly interested in child composers producing large-scale compositions before the age of 16.
Johann Nepomuk Hummel
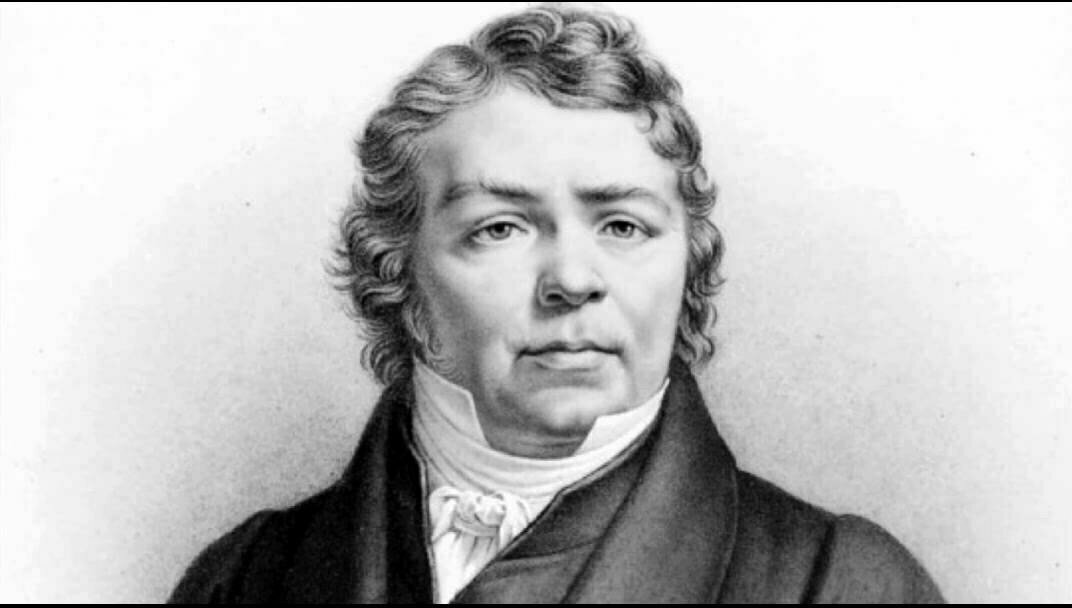

Johann Nepomuk Hummel
So let’s get started with our little survey of child prodigy composers with music by the 14-year-old Johann Nepomuk Hummel (1778-1837). Hummel studied with Mozart between the ages of eight and ten, and he composed a number of variations under Mozart’s tutelage. Once Hummel had moved to London, he published three sonatas for piano or harpsichord, two of them with violin or flute accompaniment. Hummel was only 14 at the time, “and he attracted a huge number of subscribers from London, Vienna, Prague, and countless other cities.
Gioachino Rossini
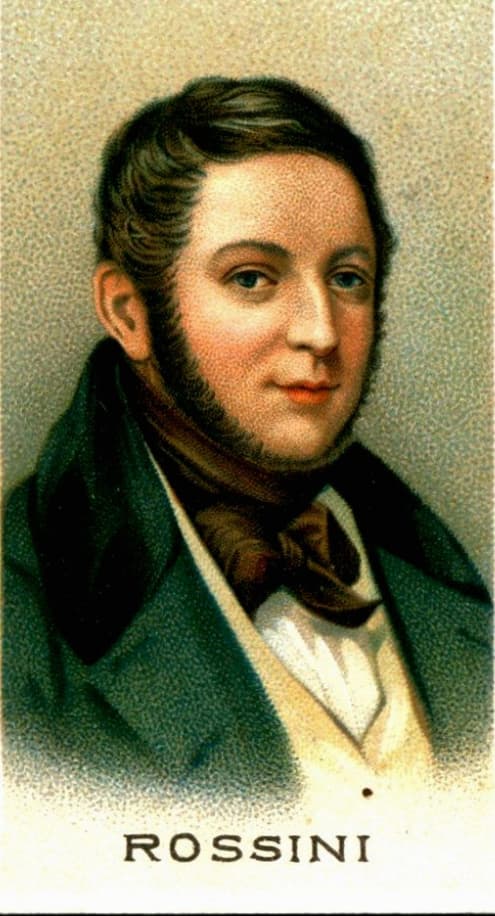

Gioachino Rossini
Gioachino Rossini (1792-1868) composed six string sonatas at the age of twelve in 1804. Scored for the unusual combination of two violins, cello, and double bass, “they are among the most successful works ever written by any child.” Rossini was familiar with the works of Mozart and Haydn, but it still seems incredible how these sonatas anticipate much of the sparkle of his later works. He composed them for a young merchant and claimed to have been ignorant of harmony when he wrote them. Actually, he described them as “horrendous,” and claimed to have written them within three days. However, Rossini could not deny his own personal style, including a characteristic melodic style, the use of crescendos, and the occasional use of the double bass as a kind of buffo character. These sonatas do show some surprisingly inventive and unusual features, “including unexpected keys and modulations, and spiced up percussive cross-relations.”
Georges Enescu
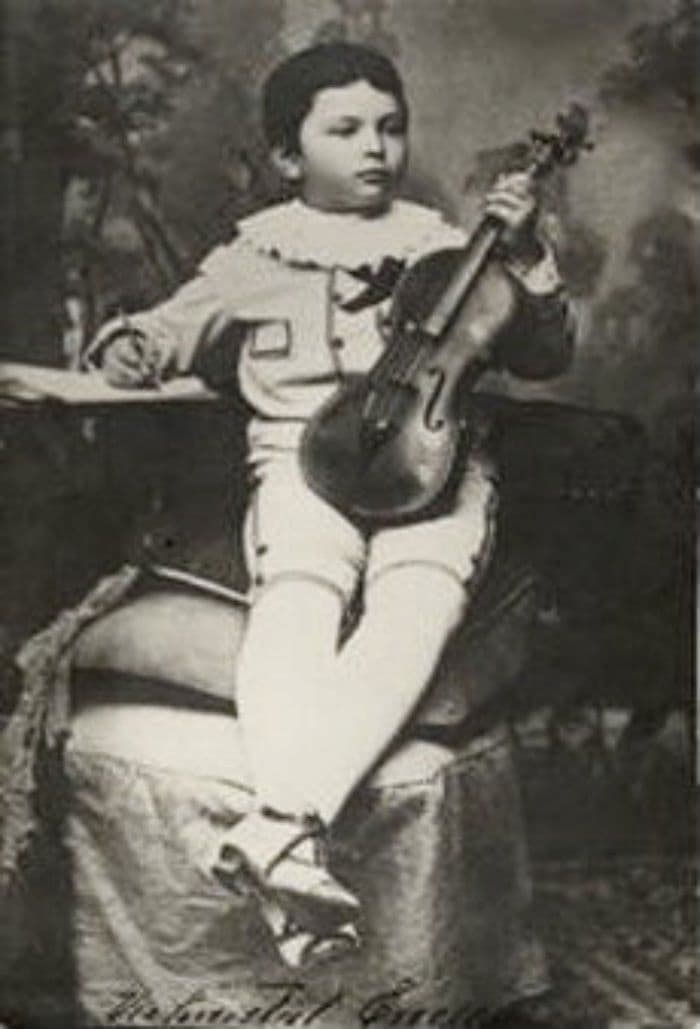

The young Georges Enescu at 3 years old
Yehudi Menuhin described Georges Enescu (1881-1955) as “the greatest musician I have ever experienced.” Such high praise is actually not surprising as Enescu had composed at least fifty works by the time he reached the age of sixteen. Almost habitually, a composer’s career is viewed as one of growth and improvements, “with the implication that early works have little or no interest.” They are often dismissed as “juvenilia,” and accorded a secondary place within the overall oeuvre. Suggestions of immaturity and youthful doodling, however, are completely out of place when speaking of Enescu. By 1895, if not before, he was “already a thorough master of the art of composition.” Enescu composed 4 Study Symphonies, and Massenet described the first symphony in D minor, as “very remarkable, extraordinary for his instinct for development.” As Cooper observes, “none of the works produced before 1897 seem to have been written with publication in mind, and indeed nearly all of them are still unpublished, though thankfully Enescu preserved the manuscripts of most of them and they are now in the Enescu Museum in Bucharest.
Frederick Arthur Gore Ouseley

Frederick Arthur Gore Ouseley
I must confess that before reading Cooper’s book on children composers, the name Frederick Arthur Gore Ouseley (1825-1889) was not known to me. As it turns out, Ouseley is “possibly the youngest child ever to compose a complete and coherent piece of music that still survives.” According to an anecdote, a very young Ouseley famously asked his father why he blew his nose in G. His father had been ambassador to Russia and Persia, and his earliest work is dated 18 November 1828, when he was aged three years and ninety-eight days. It was published many years later. These early pieces were written down by his sister Mary Jane, as Ouseley began composing long before he learned to write, “but his sister appears not to have attempted to correct his music in any way. Ouseley composed his first opera, Tom and His Mama in 1832, and most of his childhood compositions still survive, albeit only in manuscript. None of these early pieces seem to have been properly recorded. As such, I decided to feature a Prelude and Fugue written during his tenure as Vicar of St. Michael’s Tenbury as well as Warden of the College.
Muzio Clementi
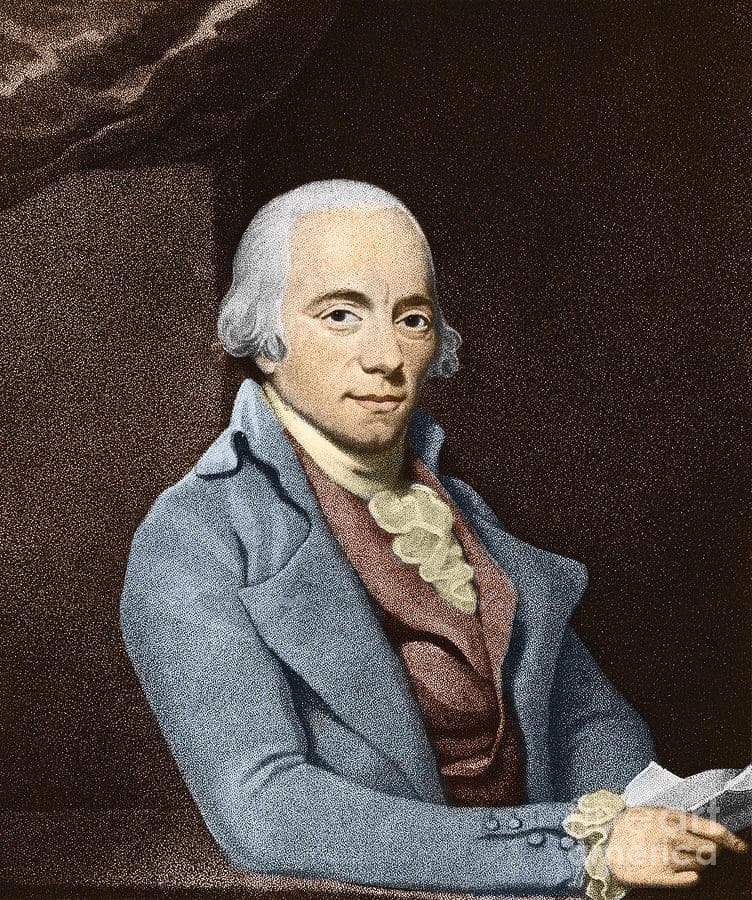
Muzio Clementi
Musicologists have discovered that Muzio Clementi (1752-1832) composed a full-scale oratorio at the age of 12. The libretto does survive in a printed source of 1764, but the music has sadly been lost. It’s almost certain that there must have been a number of additional compositions, “as the oratorio is most unlikely to be the first thing he ever wrote. Clementi’s earliest surviving work is the Sonata per cembalo in A flat major, dated 1765. The music was not published in the composer’s lifetime, but it is identified “on the manuscript as No. 20, suggesting Clementi’s prolific activity as a composer at the age of thirteen.” In three movements, the sonata, typical in many ways of its period, demonstrates Clementi’s early technical competence, with an opening classical Allegro, followed by a contrasting slow movement and a rapid finale. As a critic writes, “The sonata is a well-constructed work in which each movement explores the structural distinction between binary form and sonata form in a different way. The finale is particularly successful, with broken-chord motifs exploited in a variety of ways.”
Samuel Wesley
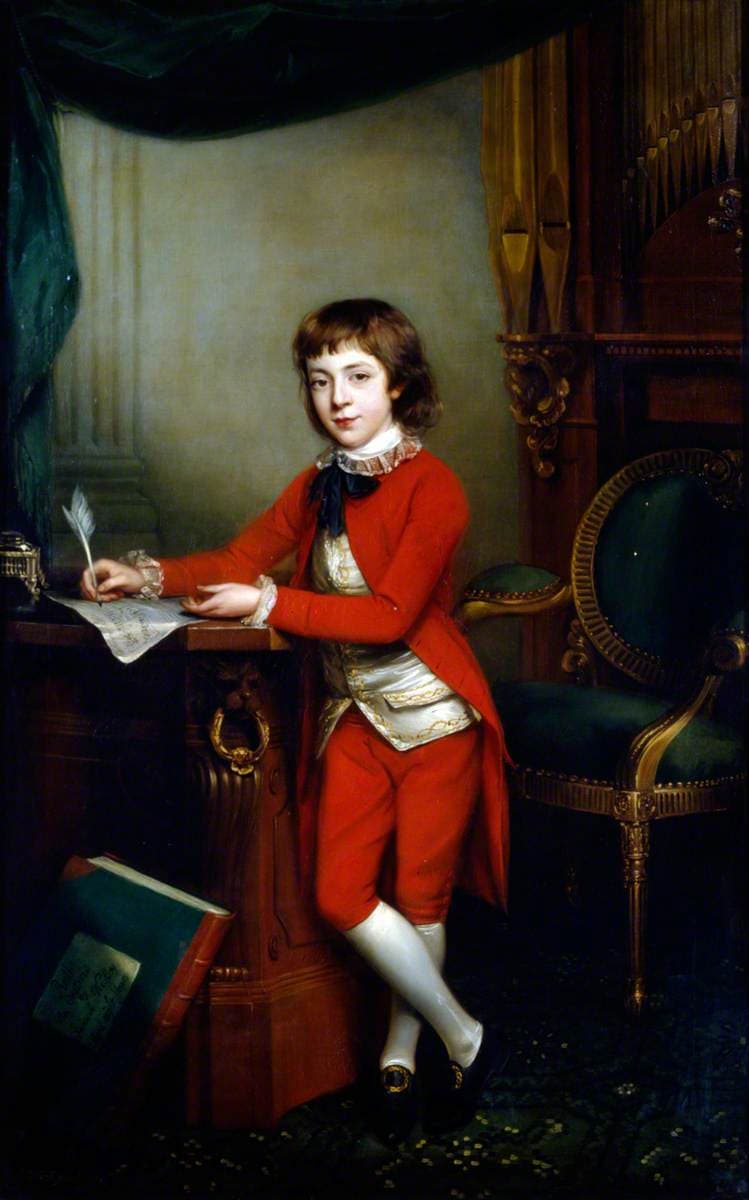

Samuel Wesley
Samuel Wesley (1766-1837) was the younger son of the divine and hymn-writer Charles Wesley (1707-1788), “the sweet singer of Methodism,” and a nephew of John Wesley, the evangelist and leader of Methodism (1703-1791). Samuel appears to have been one of the most prolific and gifted of all child composers, “as he composed more than one hundred works by the age of sixteen. By the age of eight, Wesely had crafted the oratorio Ruth, even though it was reported that much of the work had been composed up to two years earlier. A second oratorio was completed shortly thereafter. The “Sinfonia Obligato” for violin, cello and organ, with an orchestra of strings and two horns, with ad libitum timpani is dated 27 February 1781. The unusual solo grouping is used in the outer movements, and the technical demands on the three players are considerable. As Cooper observes, “By the age of sixteen Wesley had a formidable basis for developing into a truly great composer, unfortunately, he did not fulfill his potential, and the reason may be largely his own fault.” In addition, a head injury and lack of proper training prevented him from achieving his full potential.
Sergei Prokofiev

Sergei Prokofiev in 1900
Sergei Prokofiev’s (1891-1953) early compositions already show a preference for ostinato and terrifying effects. His earliest known composition is titled “Indian Galop,” and dates from the summer of 1896. As in many cases with child composers, his mother wrote it down, as the child had not yet grasped musical notation. Prokofiev continued to compose further piano pieces throughout his childhood, totaling roughly eighty works by the time he reached the age of sixteen. By 1902, Prokofiev had completed a symphony in G with the help of his teacher Reinhold Gliére. “Altogether, sixty-one pages of this symphony survive in score, including a fully orchestrated first movement and the rest in short score.” As has been suggested, however, more significant than his instrumental compositions were his early attempts at writing operas. Velikan (The Giant) dates from February to about June 1900. It is written in vocal score and divided into three acts of seven scenes. “Velikan is notable for some extreme dynamics and some powerful music for the Giant, whose footsteps are portrayed by loud, ponderous chords that uncannily foreshadow the heavy chords accompanying the main theme in ‘The Montagues and the Capulets’ in Prokofiev’s Romeo and Juliet.”
Max Bruch
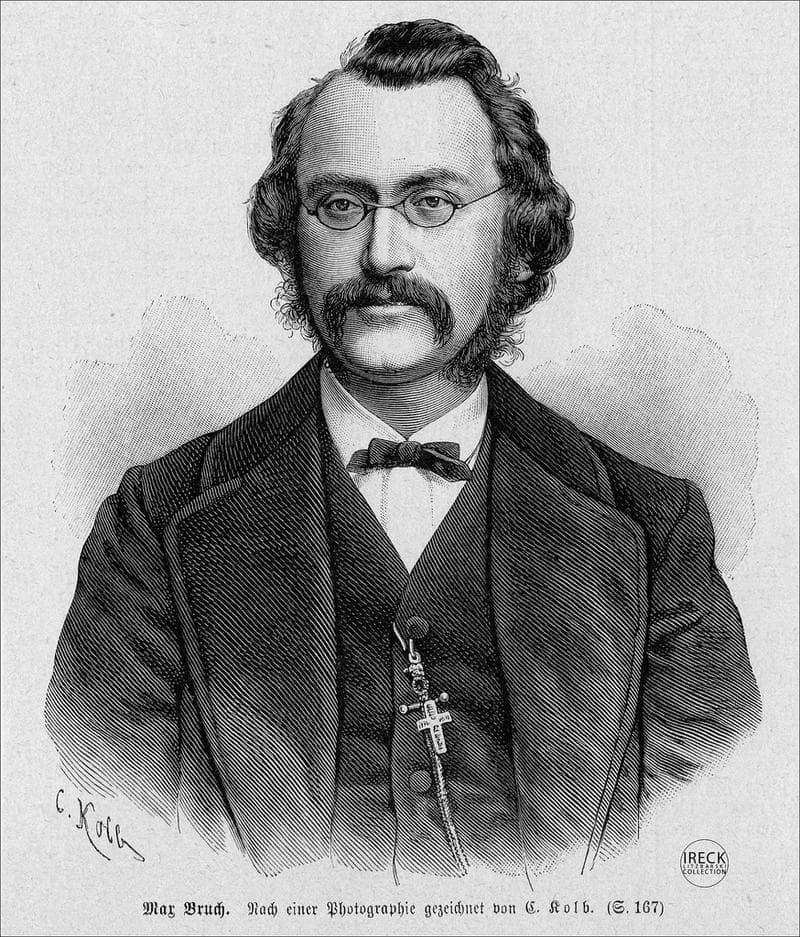

Max Bruch
The Septet in E-flat Major by Max Bruch (1838-1920) was only published in 1987, but it was composed in 1849, when Bruch was only 11 years old. Apparently, his first composition was written at the age nine for his mother’s birthday. “Soon he composed prolifically, producing motets, psalms, piano pieces, violin sonatas, a string quartet, and even orchestral works while still a child.” Almost all these early works, which also include two piano trios and lieder, have been lost. The four movements of the septet, scored for clarinet, horn, bassoon, two violins, cello, and double bass, reveal a surprising maturity. His innate musical sensitivity allowed him to orchestrate and create melodic inventions with consummate skill. Remarkable for a composer his age, Bruch creates enchanting effects, which are in marked contrast to the virtuoso elements of the work. Without doubt, this youthful composition “bears clear features of Bruch’s later style, and much skill in form and harmonic planning.”
George Frideric Handel
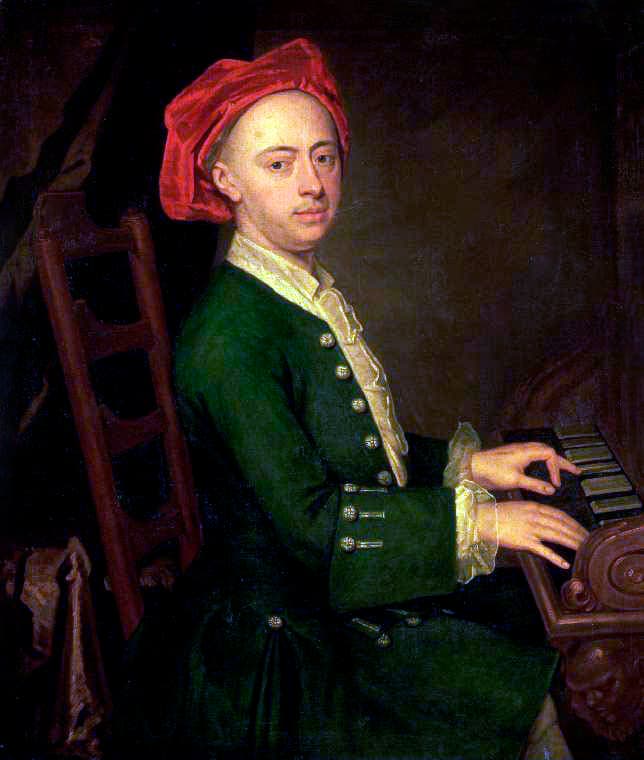

George Frideric Handel
George Frideric Handel (1685-1759) apparently composed prolifically during his childhood. He is said to have written weekly compositions for the church in Halle, but none of these early works have seemingly survived. As with many other works of Handel, we are dealing with questions of authenticity when it comes to his childhood works. He is supposed to have written six oboe sonatas at the age of eleven, “works that display occasional touches of originality.” When Handel was shown a copy of the sonatas in England many years later, he actually confirmed the authenticity of the Sonatas. He also confessed that he enjoyed writing music for the oboe. “Since they do not differ greatly in style from his later music, there seem no very reliable grounds, external or internal, for dismissing the attribution to Handel, as have been done by several recent scholars.” What makes these early works suspicious, I suppose, is that the “exhibit characteristic melodic imagination and contrapuntal skill along with Handel’s renowned ability at developing whole movements out of two or three seemingly insignificant motifs.”
Ludwig van Beethoven

Ludwig van Beethoven at 13 years old
Let us conclude this first episode dedicated to child composers with Ludwig van Beethoven (1770-1827). Many of his childhood compositions are said to be derivative of works by Mozart, however, Beethoven employs a much wider dynamic range, and much more virtuosic piano figuration. When he attached a dedicatory letter to the 1783 original edition of his three early piano sonatas (WoO 47), he explained that his Muse had commanded him to write down his music. “My Muse wished it, and I obeyed and wrote.” According to Cooper, “This sense of compulsion experienced by some composers provides further evidence for an innate, genetic predisposition to composition in a few rare children, rather than a response to an external incentive.” Beethoven’s E-flat Major Piano Concerto WoO 4, was written when the composer was fourteen years old. To enhance his son’s reputation as a prodigy, Beethoven’s father claimed that the work was written when the boy was only 12. “Beethoven was not aware of this false claim until he was 40 years old, by which time he had long since disowned the piece.” The music for this work survives in only the solo piano part, and various scholars, musicologists, and performers have since reconstructed the entire concerto. A scholar writes, “While it is difficult to regard the E-flat concerto in its standard arrangement as an authentic piano concerto by Beethoven, the parentage of the solo piano manuscript is undisputed.” Please join us next time, when we will showcase early compositions by Mozart, Mendelssohn, Clara Wieck, Richard Strauss, and others.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)