It's all about the classical music composers and their works from the last 400 years and much more about music. Hier erfahren Sie alles über die klassischen Komponisten und ihre Meisterwerke der letzten vierhundert Jahre und vieles mehr über Klassische Musik.
Wednesday, July 26, 2023
Puccini - La Bohème - Musetta's Waltz
Irish singer Sinead O'Connor dies aged 56
 Sinead O'Connor (AFP)
Sinead O'Connor (AFP)
DUBLIN (AFP) - Irish pop singer Sinead O'Connor, who shot to worldwide fame in the 1990s, has died at the age of 56, Irish media reported on Wednesday.
Her family said it was with "great sadness that we announce the passing of our beloved Sinead. Her family and friends are devastated and have requested privacy at this very difficult time," Irish national broadcaster RTE reported.
Born in County Dublin, O'Connor made 10 albums in her career from "I Do Not Want What I Haven't Got" to 2014's "I'm not Bossy, I'm the Boss", and was best known for her cover of Prince's Nothing Compares 2 U, released in 1990.
Ireland's President Michael Higgins said Ireland had lost "one of our greatest and most gifted composers, songwriters and performers of recent decades".
He praiesd O'Connor's "fearless commitment to the important issues which she brought to public attention, no matter how uncomfortable those truths may have been".
Irish prime minister Leo Varadkar said O'Connor's "music was loved around the world and her talent was unmatched and beyond compare".
"Condolences to her family, her friends and all who loved her music," he added.
Instantly recognisable with her trademark shaved head, O'Connor courted controversy throughout her career, speaking out frequently against the Catholic Church.
Iconoclast
Beginning her career busking on the streets of the Irish capital and performing in pubs, she recorded her first album "The Lion and the Cobra" -- a punk cult classic released in 1987 -- in London.
The artist said she had been abused by her mother as a child and in 1992 protested the abuse of children by the Catholic Church tearing up a picture of Pope John Paul II performing on US television programme Saturday Night Live.
In recent years O'Connor had melded her outspoken political views with spiritualism and was ordained as a priest amid controversy in 1999.
She later converted to Islam, changing her name to Shuhada' Sadaqat in 2018.
Writing on Twitter, which is being rebranded as ‘X’, Canadian singer Bryan Adams wrote "RIP Sinead O'Connor, I loved working with you making photos, doing gigs in Ireland together and chats, all my love to your family."
Irish comedian Dara O Briain said O'Connor's death came as "just very sad news. Poor thing.
"I hope she realised how much love there was for her."
Irish mixed martial arts superstar Conor McGregor commented on the singer's death writing: "The world has lost an artist with the voice of an Angel.
"Ireland has lost an iconic voice and one of our absolute finest, by a long shot. And I have lost a friend."
Moyet's 80s British pop singer Alison Moyet said O'Connor had a voice that "cracked stone with force by increment".
"As beautiful as any girl around & never traded on that card. I Loved that about her. Iconoclast," she added.
Lead singer for 90s rock band The Charlatans Tim Burgess wrote: "Sinead was the true embodiment of a punk spirit.
"She did not compromise and that made her life more of a struggle. Hoping that she has found peace."
Cultural impact
"It is hard to think of an artist who has had the social and cultural impact of Sinead," Colm O’Gorman, executive director of Amnesty International Ireland wrote in reaction to her death.
"What a loss. Heartfelt condolences to her children, her family and all who loved her," he added.
O'Connor had also spoken publicly about her mental health struggles, telling Oprah Winfrey in 2007 that she struggled with thoughts of suicide and had been diagnosed with bipolar disorder.
More recently she had shunned the limelight, in particular following the death of her son Shane from suicide last year at the age of 17.
O'Connor is survived by three children and had reportedly been dividing her time between Ireland and Britain prior to her death.
Tuesday, July 25, 2023
Why Listen to Mahler?
Memories of Alhambra - Francisco Tárrega
Never Let Me Go - Rachel Portman - We All Complete
Monday, July 24, 2023
Meet the 12 finalists of 2023 PhilPop Himig Handog songwriting festival
AT A GLANCE

Eight of the Top 12 finalists of PhilPop Himig Handog
A new batch of talented young artists will compete in this year's PhilPop Himig Handog songwriting festival. Only one of the 12 finalists will be hailed as the winner for their creative songwriting and music production.
The collaborative project, which was produced and presented by songwriting institutions PhilPop and Himig Handog, kicked off with a Digicamp series that is carefully designed to develop the skillset of aspiring participants in the fields of songwriting, music arrangement and recording, branding, marketing, career development, and intellectual property.
After a two-month workshop with some well-known musicians, including National Artist for Music Ryan Cayabyab, Jim Paredes, Paolo & Miguel Guico of Ben&Ben, Gino Cruz and more.
The entries went through multiple rounds of adjudication, headed by an esteemed panel of Board Members, producers, key leaders, prominent songwriters, and decision-makers affiliated with PhilPop and Himig Handog.
Without further ado, here are the 12 finalists with their original compositions that will compete in the PhilPop Himig Handog Songwriting Festival:
Bulacan: Rinz Ruiz – “Papahiram”
Laguna: Francis Contemplacion – “ATM”
Metro Manila: Tiara Cino – “Wag Paglaruan”
Metro Manila: Kevin Yadao – "Ghostwriter"
Metro Manila: Rob Angeles – "MHWG"
Metro Manila: Geca Morales – “Langit Lupa”
Metro Manila: Alvin Serrito – “Kurba”
Bacolod: Shantel Lapatha – “Tulala”
Cebu: Relden Campanilla – “Dili Nalang”
Cebu: Jimmy Grajo – “Salamat (Nga Wala Na Ta)”
Bohol: Keith Quito – "Buhi"
Davao: Maric Gavino – “Taliwala”
ABS-CBN Music Creative Director Jonathan Manalo stated that one of their considerations for picking the song is based on the quality of songwriting and composition.
"It was important to us that the songs were up to the standard that were set by bothPhilPop and Himig Handog. We also wanted to see how effective the fellows were in applying the lessons and insights that they've learned from the PhilPop Himig Handog DigiCamp. We wanted to challenge the fellows to break borders and push the boundaries of Filipino pop music. Lastly, we also had to factor in the appeal and marketability of the entries since our goal was also for the top songs to appeal to a wide range of Filipino music listeners," he said.
PhilPop Himig Handog Songwriting Festival is an initiative of Himig Handog and PhilPop Music Foundation. This year's game-changing event remains unwavering in its obligation to come up with innovative approaches in music-making and songwriting that are at par with international standards.
Sunday, July 23, 2023
A Pinoy-themed opening night for Broadway’s first all-Filipino musical 'Here Lies Love'
BY MANILA BULLETIN ENTERTAINMENT
AT A GLANCE
Among those who joined HLL stars Arielle Jacobs, Conrad Ricamora, Jose Llana and Lea Salonga, director Alex Timbers, producer Jose Antonio Vargas and creator David Byrne, were HLL producers H.E.R. and Jo Koy, Academy Award-winning filmmaker Spike Lee with his children Jackson and Satchel, Korean actor-director Daniel Dae Kim of “Lost” and “Hawaii Five-O”, Fil-Am actress Tia Carrere, fashion designer Josie Cruz Natori, drag queen and reality TV star Manila Luzon, and Tony Award-winning playwright David Henry Hwang (who even wore a Barong Tagalog).

The cast of 'Here Lies Love' (Images by Jenny Anderson)
On the night that the Broadway musical Here Lies Love opened at New York City’s historic Broadway Theater, the famous theater district’s environment was distinctly Filipino. The colorful jeepney was parked at the façade as the creators and cast of the musical and guests from Hollywood and the Philippines walked the red carpet.
Among those who joined HLL stars Arielle Jacobs, Conrad Ricamora, Jose Llana and Lea Salonga, director Alex Timbers, producer Jose Antonio Vargas and creator David Byrne, were HLL producers H.E.R. and Jo Koy, Academy Award-winning filmmaker Spike Lee with his children Jackson and Satchel, Korean actor-director Daniel Dae Kim of “Lost” and “Hawaii Five-O”, Fil-Am actress Tia Carrere, fashion designer Josie Cruz Natori, drag queen and reality TV star Manila Luzon, and Tony Award-winning playwright David Henry Hwang (who even wore a Barong Tagalog).

Jo Koy, one of the producers

H.E.R., one of the producers

David Byrne created the music and lyrics
Mark Bautista, who played the role of Ferdinand Marcos in the London and Seattle productions of Here Lies Love, also attended the opening, so did actresses Yassi Pressman and Yam Concepcion, HLL co-producers Bobby Garcia and Girlie Rodis, photographer BJ Pascual, and singer-actress Rachel Alejandro.
The all-Filipino cast also took the opportunity to wear the Barong Tagalog and terno to express their Filipino pride.

Tia Carrere

David Henry Hwang

Daniel Dae Kim of 'Hawaii Five O' and 'Lost'
In a review, Entertainment Weekly (EW) gave Here Lies Love a rating of “A minus,” and said, “The all-Filipino cast does a marvelous job telling the Cold War history of the Philippines and making it resonate with our current moment…” The review by EW’s Christian Holub also noted the show’s upbeat and probing qualities “Bravo to a Broadway show that's willing to ask such big questions in such an entertaining way.”

Lea Salonga

Jackson Lee, Spike Lee, and Satchel Lee

Mark Bautista, Bobby Garcia, Rachel Alejandro, and Girlie Rodis

'Here Lies Love' creative team Clint Ramos, Hal Luftig, Kevin Connor, Patrick Catullo, Jose Antonio Vargas, Diana DiMenna

'Here Lies Love' director Alex Timbers
As stellar as the cast and the production was the big passenger jeepney, an icon of Manila, which was emblazoned with the musical’s title on the side. The cast couldn’t resist having their photos taken there.
For updates about the musical, visit herelieslovebroadway.com and follow herelieslovebway on Facebook, Instagram, YouTube and TikTok.
Saturday, July 22, 2023
The Filipinization of the French comic ballet Coppelia
Ballet Philippines to showcase Filipino performative art in this classic piece with stronger dancing and technically demanding choreography.
AT A GLANCE
Style, technique, and character are the focal points of Ballet Philippines' 54th season and Coppelia highlights these aspects in splendid fashion.
By JAMES SAM
Ballet Philippines’ 54th season is opening with a Filipino rendition of Coppelia. Originating in 1870 from Paris Théâtre Impérial l’Opéra, the story is centered around Dr. Coppelius’ daughter, a life-like doll, and her sudden presence at a town festival where two youths, Franz and Swanhilda, plan to marry. Franz, becoming infatuated with the doll, shifts his attention away from Swanhilda and in an attempt to win her betrothed back, Swanhilda decides to impersonate the beautiful, life-size doll. A hectic series of events follows, concluding with a narrative that places love above all.

Swanhilda played by Jemima Reyes
A pandemic-stricken Ballet Philippines, in anticipation of its return to live performances, dons the title “Power of Dance.” Dedicated to sharing the passion of ballet to their audience, the company aims to reinvigorate the performance arts in the Philippines and elevate the experience to new heights.
According to Kathleen Liechtenstein, president of Ballet Philippines, the show is suitable for all ages. A family-bonding experience calling for introspection and self-discovery, Coppelia aims to inspire from the company’s new home at the Theater at Solaire.

Coppelia played by Idelle Buhia
Mikhail Martynyuk describes the show as a great brightness filled with powerful dances. Having debuted as the lead performer of Coppelia, Ballet Philippines’ artistic director carries with him a wealth of knowledge garnered from 24 performances of the show in Spain. In his desire to showcase the strength and talents of Ballet Philippines’ dancers, Martynyuk’s Filipino adaptation of Coppelia incorporates stronger dancing and technically demanding choreography.

Franz played by Ian Ocampo
“If you have style, you need to have technique,” said Martynyuk at a press preview, “If you have technique, you need to have character.” Style, technique, and character are the focal points of Ballet Philippines 54th season and Coppelia highlights these aspects in splendid fashion.
Hosted at The Theatre At Solaire, Ballet Philippines’ Coppelia will run from Aug. 4 to 6. Tickets are available online at ballet.ph.
The enduring legacy of Arturo Toscanini: ‘a life force from a vanished age
The enduring legacy of Arturo Toscanini: ‘a life force from a vanished age whose work refuses to date’
Richard Osborne
Monday, July 3, 2023
‘Toscanini was a classicist at heart, with a classicist’s love of light, logic, orderliness and physical beauty’

Arturo Toscanini was born 10 years before the invention of the phonograph yet remains a living presence because of it, a life force from a vanished age whose work refuses to date.
His first recordings were pre-electric, made with players from La Scala, Milan, on tour in the United States in 1920; his last, completed in New York in 1954 at the age of 87, was an account of Verdi’s Un ballo in maschera that remains the most elemental and erotically charged of all accounts of the piece. ‘I think that Toscanini’s small orchestra is the most effective of all on the gramophone,’ said Compton Mackenzie of that 1920 recording of the finale of Beethoven’s Fifth Symphony, writing in the inaugural issue of The Gramophone in April 1923.
Toscanini possessed two qualities that were invaluable for recording: first, the purity and beauty of sound any Toscanini-trained orchestra presented to the microphones; secondly, a conducting style, shorn of all mannerism, that bore repeated hearing. To which, writing in November 1926, Mackenzie added a third: the electric charge of the conducting. What might seem vivid in the concert hall doesn’t necessarily make a comparable impact on record; and where recorded impact was concerned, Mackenzie suggested, Toscanini was ‘supreme’.
It was principally through the gramophone that Toscanini became the most venerated conductor of his age – ‘iconic’, as latter-day usage would have it. As to the actual iconography, that, too, made an early appearance in The Gramophone in January 1930 in the form of a caricature in the Italian Futurist style by Fernando Autori. It was the image chosen to accompany the publication’s first full-length profile of Toscanini, written not by the editor but by his wife, the pianist, writer and all-round woman of culture Faith Compton Mackenzie. It’s a most revealing piece, not least because of the insights it gives into Toscanini’s relations with the four composers with whom he was most closely associated: Verdi and Puccini, both of whom he worked with and knew, and the two giants of 19th-century German music, Beethoven and Wagner.

The profile of Toscanini from the January 1930 issue of Gramophone by Faith Compton Mackenzie
Virtually unknown outside Italy and the United States, even as late as 1930, Toscanini had long been a household name to the Mackenzies, partly owing to Faith’s extended residence on the Italian island of Capri in the 1910s and her intimate relationship with Renata Borgatti, the piano-playing daughter of revered tenor Giuseppe Borgatti – Toscanini’s Siegfried and Tristan in groundbreaking Wagner performances in turn-of-the-century Italy.
Not the least of Toscanini’s achievements was the skill with which he grafted Austro-German music onto Latin rootstock, and vice versa. This was heard to particular effect in his conducting of the Beethoven symphonies, of which Mrs Mackenzie gives an eloquent report. His reputation as a Wagner conductor, however, stretched back further, to a performance of Tristan und Isolde which the composer’s son, Siegfried, heard in Turin in 1901.
This was an era, it’s worth remembering, in which Wagner could do no wrong and most Italian opera – all but a handful of acknowledged masterpieces – was treated as little more than cheap entertainment. Mrs Mackenzie cites La traviata, whose tunes had become ‘stale, clotted and worn with careless use; we have heard it described as quaint and ridiculous, and perhaps we have agreed.’ But with Toscanini in charge, ‘It is almost with a caress that the lion of conductors draws out the familiar melodies that tell the poignant tale of Violetta.’
Toscanini’s first appearance on the cover of The Gramophone was in May 1942, shared with his son-in-law Vladimir Horowitz at the time of the release of their famous recording of Tchaikovsky’s First Piano Concerto.

His first solo cover, in June 1949, was linked to his recording of extracts from Berlioz’s Roméo et Juliette. Inside that edition, the disc was subject to a blistering attack, not on Toscanini’s conducting, but on the NBC recording. The review was by the first of a new breed of Gramophone reviewers drawn from the higher echelons of the BBC music department, the 34-year-old Lionel Salter, who clearly knew what he was talking about.

Toscanini liked the restricted ambience of NBC’s Studio 8H, given that he could hear everything from the rostrum. What was problematic was not so much the studio or its equipment (16- and 17-inch wide-groove acetate discs revolving at 33/3rpm) but erratic microphone placements and the often poor quality of the commercial transfers.
One of the great ‘ifs’ regarding Toscanini’s legacy is what might have happened had the rise of Fascism and the Second World War not intervened, tying him to the United States, an American radio orchestra and radio station production values.
In a fascinating reminiscence by John Amis, ‘Legge on Toscanini’, published in Gramophone in June 1990, we learn that EMI’s Walter Legge had the temerity to tell Toscanini that the tempos in his 1946 broadcast recording of La traviata were mostly too fast. Toscanini asked why he thought this, but later conceded that he’d lacked a suitable producer at NBC – someone who would dare advise him, as we know Legge advised Sir Thomas Beecham, Victor de Sabata, Herbert von Karajan and other stellar talents with whom he worked and frequently did battle. Not that the American-made recordings obscure the essential nature of Toscanini’s genius. Mackenzie spoke of Toscanini’s ‘impact’ on record, much as philosopher Sir Isaiah Berlin, who heard him regularly in London and Salzburg in the 1930s, spoke of ‘the intensity, the seriousness, the sublime terribilità’ of his conducting. ‘One left the concert hall or opera house’, he told me, ‘convinced that this, and only this, was the truth.’
Poet, polymath and part-time music critic Ezra Pound – a familiar of the Mackenzies and a good friend of Renata Borgatti – defined another aspect of Toscanini’s craft as his ability to sustain the cumulative effect of an exact rhythm more perfectly, and over a longer period, than ‘temperamental and moody performers’ thought of attempting. (Go to Toscanini’s superb 1953 recording of Berlioz’s allegedly loosely written Harold in Italy to get a sense of what Pound was driving at.)
The words ‘temperamental’ and ‘moody’ may have been aimed at Serge Koussevitzky or, more generally, Wilhelm Furtwängler. If the latter, it was a perpetuation of one of performing history’s most futile jousts. Writing in 1939, Neville Cardus described Toscanini’s Beethoven as ‘the most musically comprehensive of our time, if not the most poetically comprehensive’. The fact is, we needed Toscanini’s Beethoven and Furtwängler’s. If Toscanini was peerless in the Seventh Symphony and Furtwängler in the Eroica, in the Ninth both were needed, according to one’s mood or inclination.
Toscanini was a classicist at heart, with a classicist’s love of light, logic, orderliness and physical beauty. It’s an approach that didn’t cover all eventualities, but it served. ‘He has soul, poetry, flexibility, dash, refinement, dramatic instinct,’ wrote Puccini in 1922. ‘In short, a real miracle.’
Friday, July 21, 2023
Jane Stirling: Why Did This Piano Student Pay for Chopin’s Funeral?
by Emily E. Hogstad, Interlude
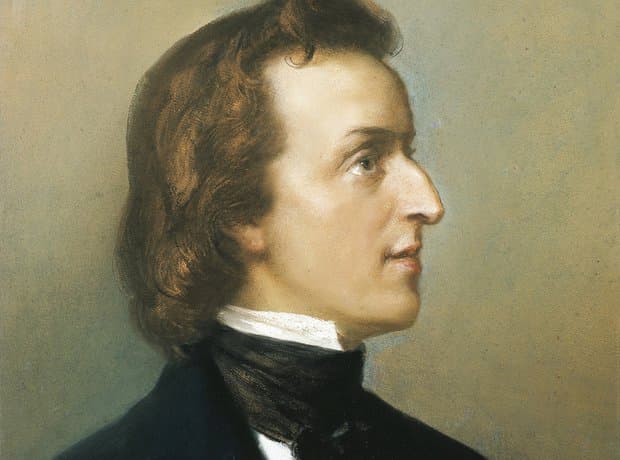

Frédéric Chopin © ClassicFM
Jane Stirling’s Childhood
Jane Wilhelmina Stirling was born 15 July 1804 in Perthshire in central Scotland. She was the daughter of John Stirling of Kippendavie, a wealthy landowner who had property in Scotland and the West Indies, and his wife Mary.
Jane was born into a big family: she had twelve older siblings! Tragically, her mother died when she was a child, and then her father died a few years later. The grieving teenage heiress moved in with her older sister Katharine Erskine, a young and independent widow.
Despite the tragedies of her teenage years, Stirling proved to be a social butterfly. She loved the arts, playing the piano, and going to dances and balls. As the legend goes, over thirty men proposed to her, but she turned them all down because she never fell in love with any of them.
Young Adulthood in Paris
In 1826, when Stirling was twenty-two, her older sister brought her to Paris. The sisters loved the city so much that they began to live part-time in France.
When the time came for Stirling to choose a Parisian piano teacher, she chose Frédéric Chopin, a mutual acquaintance of her former teacher, pianist Lindsay Sloper. Chopin and Stirling became friends. Chopin respected her and her musicianship enough to pass along one of his students to her, and in 1844, she was thrilled to find out that he dedicated two nocturnes to her (the pair in his op. 55).
At the time, Chopin was in the midst of an unraveling relationship with author George Sand, and he was trying to come to grips with his new lifestyle. Stirling wanted to help. So they came to an unconventional arrangement: Stirling would serve as a kind of agent and business manager to help keep Chopin’s life running smoothly. She even took on arranging his concerts and worked with him on assembling the French-bound volumes of his works.
George Sand’s daughter wrote about Stirling and Erskine:
“During lessons, when you visited the Master you could meet two tall persons, typical Scottish women, skinny, pale, in indefinite age, serious, dressed in black, never smiling. Under this quite gloomy appearance, there were lofty, noble, and devoted hearts.”
Chopin’s Helper
Stirling seems to have been rather omnipotent in Chopin’s life during this time. She saw to all of the details of his famous Salle Pleyel concert in February 1848, down to the temperature of the auditorium and the choice of flowers. He played a Mozart piano trio, his cello sonata, and some relatively undemanding pieces for solo piano. After the concert was done, he staggered backstage to Stirling and collapsed in her arms. It would be his last Paris concert. In March, revolution broke out, and many of Chopin’s aristocratic supporters fled the country.
A couple of months later, Stirling arranged for him to visit London. Chopin dreaded the rigors of traveling, but he needed the money badly, so in the spring of 1848, they set off together.
Chopin’s Last Tour – And a Proposal?
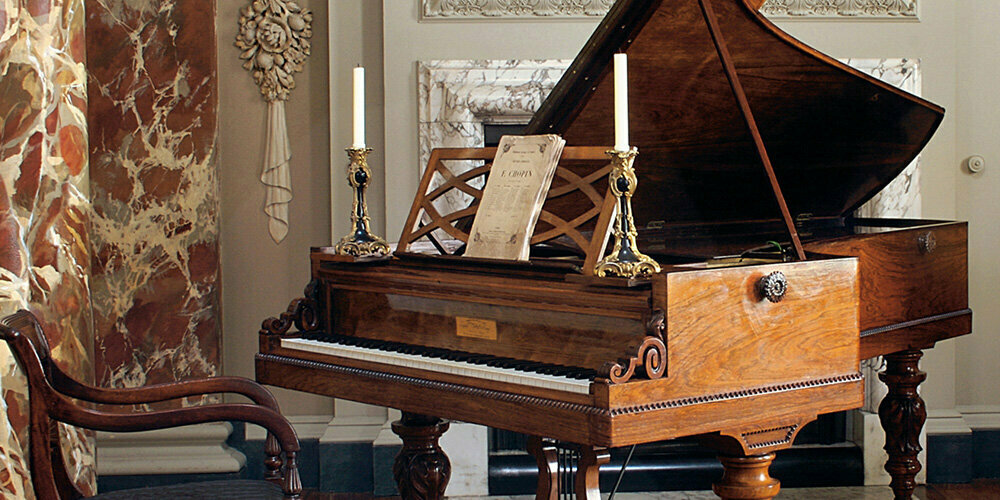

Chopin’s Pleyel grand piano, 1848 (The Cobbe Collection, UK)
While in London, Chopin ended up keeping three pianos in his room from three different makers. His furious landlord doubled the rent, but Stirling stepped in to cover the cost for him. The social highlight of this English visit came when he performed for Queen Victoria and her husband Prince Albert at a private party.
After the stay in London, he took the train to Edinburgh, per Stirling’s suggestion. He played in Manchester, Glasgow, and Edinburgh. Tickets were expensive – and Jane purchased many of them herself, then gave them away for free. Ominously, while Chopin was in Edinburgh, feeling that he would not live much longer, he drew up a will.
Rumors swirled of an impending engagement between the sick man and his energetic promoter, but Chopin never made a formal offer of marriage. Something about Stirling grew to irritate him – maybe his growing weakness and his increasing dependence on both her and her sister. He wrote things to friends like “A rich woman needs a rich husband” and “They have married me to Miss Stirling; she might as well marry death.” The sisters’ enthusiastic promotion of Protestantism was also proving to be extremely grating.
Chopin’s Death and Its Aftermath
In November 1848, Chopin left the gloomy British Isles to return to Paris. He was deeply in debt, and Stirling quietly paid those debts off. His condition only deteriorated. Over the course of 1849, it became clear that Chopin’s death was imminent. After much suffering, in October he passed away from what is generally believed to have been tuberculosis.
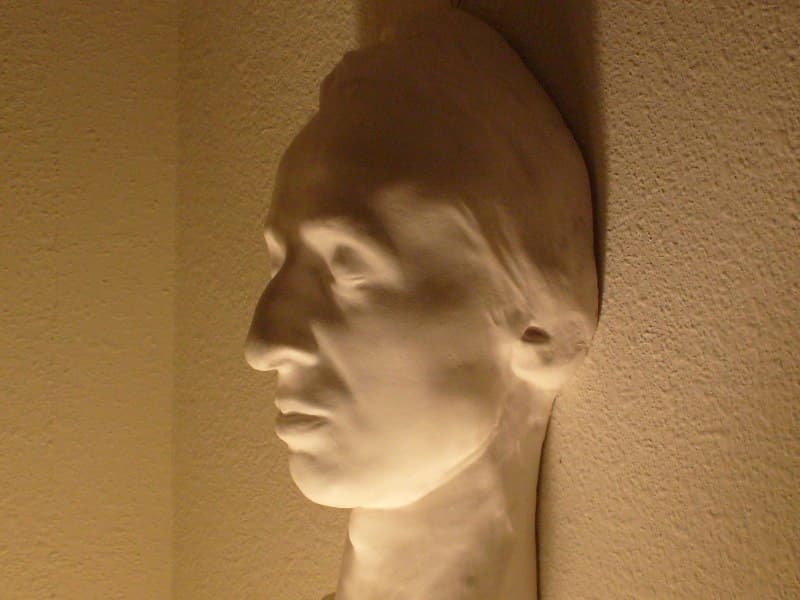

Chopin’s death mask © Wikipedia
After he died, Stirling dressed in mourning black, as if her husband had passed away. She paid the cost of his extravagant funeral at Paris’ famous La Madeleine (although Chopin’s sister Ludwika eventually paid back the cost), and it was attended by thousands. Fearing unscrupulous thieves or souvenir hunters, it is believed by historians that she was likely the anonymous buyer who purchased much of Chopin’s estate, including his famous death mask, to distribute to those who loved him. She also saw that his preserved heart would be brought from Paris to Warsaw.
A portrait she’d commissioned of Chopin by Polish artist Teofil Kwiatkowski turned into a deathbed portrait. Pictured in the portrait is Chopin, dressed in white, and surrounded by the dark-clothed figures of author Aleksander Jełowicki, Chopin’s sister Ludwika, piano student Marcelina Czartoryska, Polish politician Wojciech Grzymała, and the artist. Stirling is nowhere to be found: she’s already slipping into the background of the historical record.
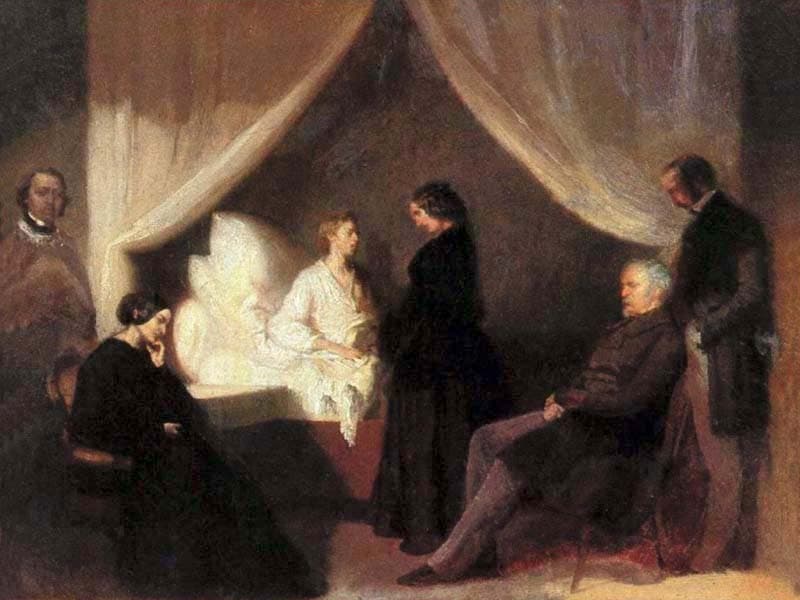
Chopin on His Deathbed, by Kwiatkowski, 1849, commissioned by Jane Stirling.
To mark the first anniversary of his death, Stirling wrote to Ludwika asking for a handful of Polish soil so that she could sprinkle it on Chopin’s grave. The request was granted. In a particularly moving gesture, Stirling paid to have one of Chopin’s pianos shipped to Ludwika, and the two women carried on a considerable correspondence after his death, tending to matters of his legacy.
Intriguingly, according to legend, Chopin told Stirling – and Stirling alone – his true date of birth. She is said to have written it down, placed it in a box, and buried it with him.
Stirling’s Post-Chopin Life and Legacy
Stirling lived for another decade after Chopin’s death and died of an ovarian cyst in 1859. She never married. She left most of Chopin’s estate to his mother. It ended up in a palace in Warsaw, where it was destroyed by Russian troops in 1861.
Jane Stirling may not be nearly as famous as Chopin’s other caretaker figure, George Sand, but she was certainly one of his most faithful friends and one of the people we have to thank today for helping to preserve the rich musical legacy that her friend and teacher left behind.